Techniques for adaptive equalization of digital communication systems Abstract. Linear least mean square LMS equalizers with binary phaseshift keying BPSK in dispersive multipath channels and additive white Gaussian noise AWGN.
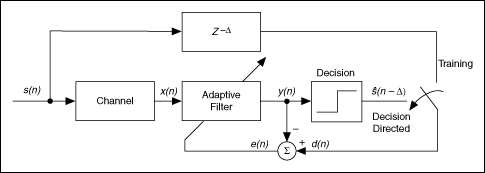
Equalizer works like an inversed filter which is placed atthe front end of the receiver.
Adaptive equalization in digital communication. This chapter presents Simulink models that incorporate adaptive equalization. Linear least mean square LMS equalizers with binary phaseshift keying BPSK in dispersive multipath channels and additive white Gaussian noise AWGN. Linear LMS equalizer with quadrature phase shift keying QPSK in a channel with Intersymbol.
An adaptive equalizer is a digital circuit that compensates for a digital signals in-channel complex frequency response impairments. The cable industry has long used the term frequency response to describe amplitude or magnitude-versus-frequencythat is what is seen on the display of test equipment used to sweep outside plant. Chapter 12 Adaptive Equalization in Digital Communications 121 Adaptive Equalization.
This chapter presents Simulink models that incorporate adaptive equalization. Specific topics include the following. Linear least mean square LMS equalizers with BPSK in dispersive multipath channels and AWGN including Sample based.
Equalization plays a vital role in many modern communication systems. Adaptive equalization is a particular example of adaptive signal processing. It is an important technique to combat distortion and interference in communication links.
The approach which is conventional to communication channel equalization is based on adaptive linear system theory. The present paper extends the utility of this automatic equalization system by permitting it to change settings during the data transmission period in response to changes in transmission channel characteristics. Three schemes for accomplishing this adaptive equalization without the use of test signals are described and evaluated analytically.
Adaptive equalization can be used to improve digital data transmission on wireless links with time-varying multipath distortion. This paper summarizes some of the performance aspects of adaptive equalization in wireless applications. After outlining the need to counter intersymbol interference ISI in high-rate data transmission over time-varying.
Hence various algorithms for adaptive channel equalization have been developed and applied to compensate for the non-ideal characteristics of the communication channel. Adaptive algorithms can be divided into two classes according to the type of the error function being minimized 346. An adaptive equalizer is an equalizer that changes their properties automatically wrt time of communication channel.
It is generally used with coherent digital. The zero-forcing linear equalizer should be selected such that the resulting Gfldexpj2πfT is constant equalized in order to eliminate all ISI Equalizer transfer function TELIN 30 Zero-forcing linear equalizer 6 The ZF-LE is not unique. Different choice of Hrecf yields a different equalizer and a different PnoisePuseful Ce Ge jfT.
Techniques for adaptive equalization of digital communication systems Abstract. A previous paper described a simple adjustment algorithm which could be employed to set the tap gains of a transversal filter for the equalization of data transmission systems. In the case of a linear communication channel eg a telephone channel used for digital data transmission the traditional form of an adaptive equalizer consists of a relatively long tapped-delay line filter whose tap-weights are adjusted in accordance with the LMS algorithm Qureshi 1985.
Equalizers Adaptive channel equalizers have played an important role indigital communication systems. Equalizer works like an inversed filter which is placed atthe front end of the receiver. Its transfer function is inverse tothe transfer function of the associated channel is able toreduce the error causes between the desired and estimatedsignal.
This is achieved through a process of. Adaptive equalizer is to operate on the channel output such that the cascade connection of the channel and the equalizer provides an approximation to an ideal transmission medium. Austin Decision-Feedback Equalization for Digital Communication Over Dispersive Channels MIT.
Lincoln Laboratory Lexington Mass August 1967. Reliable wireless digital communication namely Inter-Symbol Interference ISI the intensity of which makes the channel noise inconsequential. The theoretical background for wireless channels modeling and adaptive signal processing are covered in first two chapters of dissertation.
The thesis is focused on the problem of equalization in digital communication systems. Theoretical part includes brief observation of different approaches of equalizer designing. The practical part deals with implementation of the most often used equalizers and their adaptation algorithms.
Digital Equalizer RS232 UART Codec Video-in or audio-in Video or audio interface Signal generator or PC Dispersive channel PC BER calculation random gen. Seed signal Overview Initial Goals The purpose of this project is to build an adaptive equalizer on FPGA to equalize asynchronous serial data that have been distorted by a certain channel.
