At 25 per cent block it was no longer observable in five of six preparations. Although the mechanism of action of alpha-latrotoxin is not known it does require binding of alpha-latrotoxin to a high-affinity receptor on the presynaptic plasma membrane.
Lα-bungarotoxineα-BTX est lune des bungarotoxinesentrant dans la composition du venin des serpents du genre Bungarus.
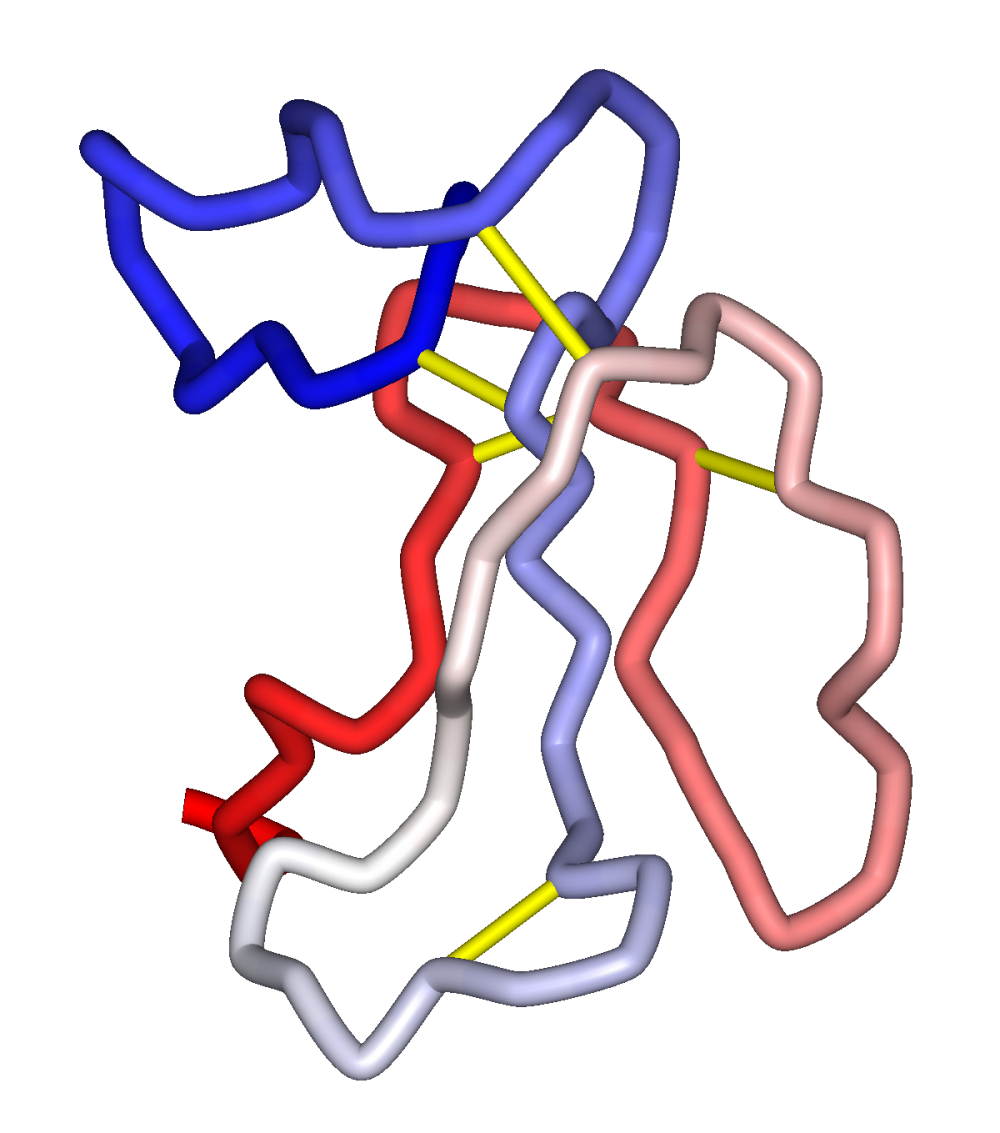
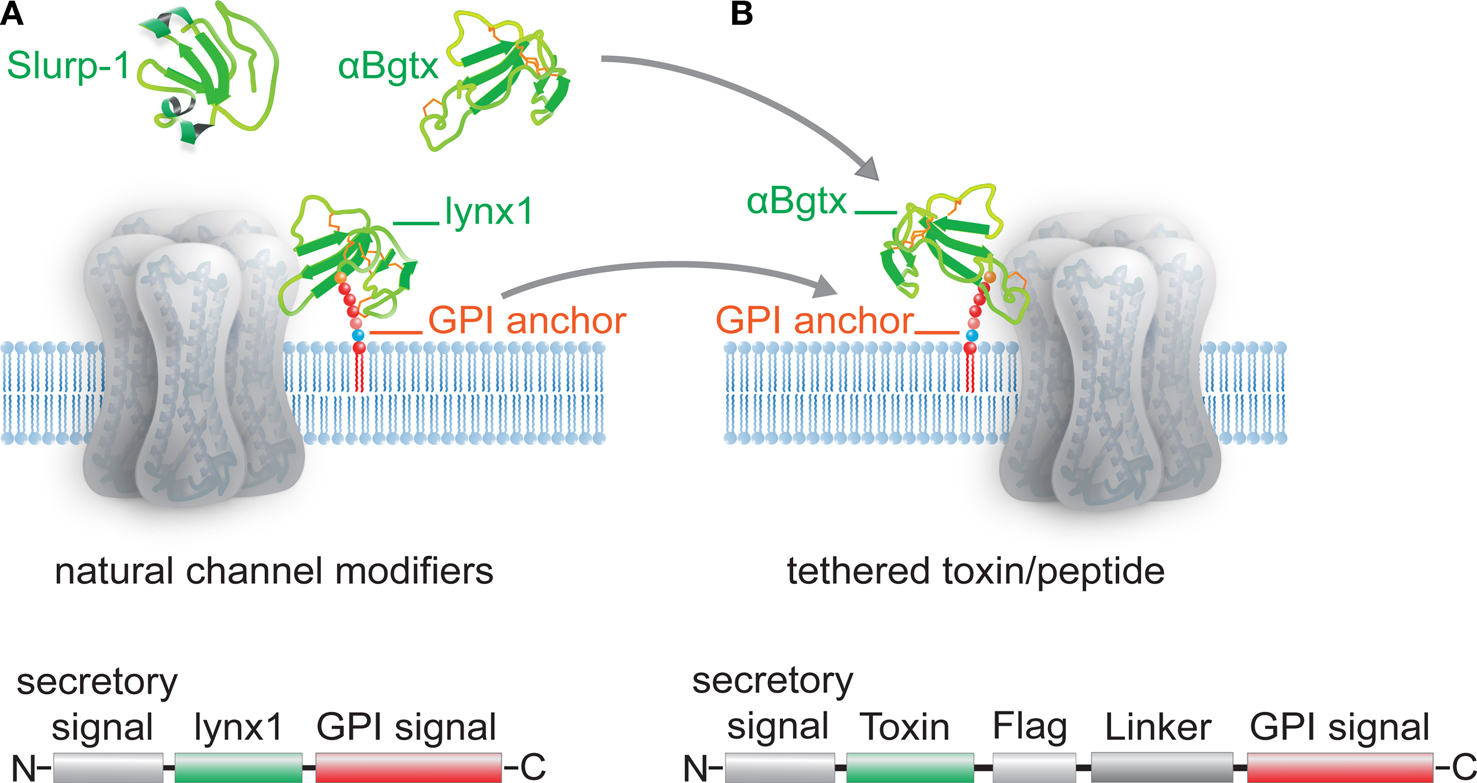
Alpha bungarotoxin mechanism of action. Alpha-bungarotoxin α-BTX is a neurotoxin contained in the venom of the Taiwanese many-banded krait. It produces paralysis of striated muscles by blocking cholinergic receptors in the neuromuscular junction. The toxin also blocks a subtype of neuronal cholinergic receptor α7 located in the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Bungarotoxins are a group of closely related neurotoxic proteins of the three-finger toxin superfamily found in the venom of kraits including Bungarus multicinctus. α-Bungarotoxin inhibits the binding of acetylcholine ACh to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. β- and γ-bungarotoxins act presynaptically causing excessive acetylcholine release and subsequent depletion.
Both α and β forms have been. α-BUNGAROTOXIN binds nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and has been used to isolate and study them. It blocks neuromuscular transmission by irreversible binding to motor end-plate acetylcholine receptor but does not depress acetylcholine release from motor nerve endings.
α-Bungarotoxin α-BuTx has been shown to bind mainly to sequences around the two cysteines at. ALPHA - BUNGAROTOXIN The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor nAChR carries two binding sites for snakes venom neurotoxins. A-Bungarotoxin from the Southeast Asian Krait is a long neurotoxin which competitively blocks AChR at the acetylcholine binding sites in.
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor AcChoR is a ligand-gated ion channel that is activated upon binding of acetylcholine. α-Neurotoxins in particular α-bungarotoxin α-BTX bind specifically and with high affinity to the AcChoR and compete with binding of the natural ligand. We employed a 15-mer phage-display peptide library to select epitopes reacting with α-BTX.
Effect of alpha-neurotoxins from snake venoms alpha-bungarotoxin and alpha-cobratoxin 10-6M on the ACh-induced current and on the fast excitatory postsynaptic current EPSC were studied in voltage-clamped neurons of the isolated rabbit superior cervical ganglion treated with atropine 10-6M alpha-Neurotoxins produced potentiating or inhibitory effects on ACh-induced current and only inhibitory effect on EPSC. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor nAChR carries two binding sites for snake venom neurotoxins. Alpha-Bungarotoxin from the Southeast Asian.
α-Bungarotoxin isoform A31 is a 74 amino acid peptidyl toxin isolated from the venom of the banded krait snake Bungarus multicinctus 1. α-Bungarotoxin blocks postsynaptic neuromuscular transmission via competitive inhibition of nicotinic ACh receptors nAChR s with an IC 50 of 35 x 10 -10 M thereby preventing the depolarizing action on postsynaptic membranes and blocking. Although the mechanism of action of alpha-latrotoxin is not known it does require binding of alpha-latrotoxin to a high-affinity receptor on the presynaptic plasma membrane.
The actions of these venom toxins can be broadly divided into those with presynaptic and postsynaptic loci. The postsynaptically acting toxins characterized by the snake alpha toxins α-bungarotoxin will be considered later in this chapter. These latter toxins have proven to be vital tools in characterizing identifying and isolating the nicotinic AChR.
In control preparations alpha-bungarotoxin irreversibly blocked depolarization produced by carbachol. However after receptor desensitization alpha-bungarotoxin was no longer effective in blocking the response to carbachol. It is concluded that desensitization protects cholinoceptors from the action of alpha-bungarotoxin.
The α-neurotoxins from snake venom α-bungarotoxin and α-cobratoxin in a concentration of 10 6 M caused an increase in amplitude potentiation of the acetylcholine current inhibition of that current or initial potentiation followed by inhibition in different neurons. Spectral analysis of the fluctuations of this current showed that α-neurotoxins affect neither the current through a single. β-Bungarotoxin is a form of bungarotoxin that is fairly common in Krait Bungarus multicinctus venoms.
It is the prototypic class of snake β-neurotoxins. There are at least five isoforms coded β 1 to β 5 assembled from different combinations of A and Bchains. The toxin is a heterodimer of two chains.
Edrophonium-induced contracture of the muscle was blocked by alpha-bungarotoxin only. At 25 per cent block it was no longer observable in five of six preparations. Beta-bungarotoxin enhanced the contracture.
At complete block the contracture reached 156 SE 11 n 6 per cent of control. The authors conclude that edrophonium facilitates neuromuscular transmission by a prejunctional. The facilitatory action was blocked by the nicotinic acetylcholine ACh receptor antagonists alpha-bungarotoxin and mecamylamine.
A similar facilitation was induced by the other nootropic agents piracetam and aniracetam but the facilitation was not inhibited by nicotinic ACh receptor antagonists and it did not occlude the potentiation induced by nefiracetam. In the Xenopus oocyte expression systems. Lα-bungarotoxineα-BTX est lune des bungarotoxinesentrant dans la composition du venin des serpents du genre Bungarus.
Il sagit dune α-neurotoxine consistant en un polypeptidede soixante-quatorze acides aminés antagoniste compétitif des récepteurs. The interactions of alpha-bungarotoxin or tubocurarine with the neuromuscular block and endplate depolarization induced by succinylcholine SCh in the phrenic nerve-diaphragm preparation of mice were studied in order to elucidate the role of depolarization by SCh in the neuromuscular blockade. The SCh concentrations required to depress the indirect twitch response by 20 and the.