
They include covalent species onium ions and carbenium ions of different degrees of association. The polymerization of ethene by an ionic or freeradical reagent AB is an example.
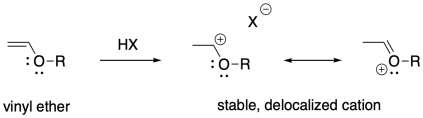
In the current theory of the cationic polymerizations of alkenes the initiation is visualized as the addition of the cationic moiety say R of an initiator to the double bond of the monomer thus generating a carbenium ion at the other end of the double bond and that reaction is replicated by the reaction of the new carbenium ion with more monomer.
Cationic polymerization of alkenes. Polymerization of Alkenes 10-8A Anionic Polymerization. Anionic polymerization of alkenes is quite difficult to achieve because few anions or. Polymerization of an alkene by acidic reagents can be formulated by.
The cationic polymerization of alkenes and heterocyclics is compared in a critical way. After a brief introduction to the polymerizability of various monomers and efficiency of initiators various active sites involved in propagation are discussed. They include covalent species onium ions and carbenium ions of different degrees of association.
Polymerization of Alkenes 10-8A Anionic Polymerization. Anionic polymerization of alkenes is quite difficult to achieve because few anions or. Polymerization of an alkene by acidic reagents can be formulated by.
Q Cationic polymerization of simple alkenes is especially efficient for alkenes which form relatively stable carbocations note the tertiary carbocation intermediate and which have one double bond terminus of the alkene unsubstituted so as to minimize steric effects in the TS for the addition reaction. This unified presentation of cationic polymerization discusses initiation propagation transfer and termination in cationic polymerizations of alkenes and heterocycles. It also elucidates the mechanisms of the reactions involved in all carbocationic and ring-opening polymerizations.
An unprecedented capacity of hexafluoroiso-propanol to serve both as a sole proton source and polar medium in the cationic polymerization of β-pinene is disclosed. The elaborated procedure is simple-to-operate. It furnishes the respective polymer in a nearly quantitative yield.
This unified presentation of cationic polymerization discusses initiation propagation transfer and termination in cationic polymerizations of alkenes and heterocycles. It also elucidates the mechanisms of the reactions involved in all carbocationic and ring-opening polymerizations. Polymerization is a process by which an organic compound reacts with itself to form a highmolecularweight compound composed of repeating units of the original compound.
The polymerization of ethene by an ionic or freeradical reagent AB is an example. Living cationic only possible for a specific subset of monomers Most industrial cationic processes are not living - recent developments are improving this Kinetic Steps for Cationic Polymerization Initiation. Use Acids Protonic Acids Bronsted.
HA strong but without nucleophilic counterion HClO 4 CF 3SO 3H H 2SO 4 CFCOOH comes off. Cationic polymerization is performed to produce oligomers and high polymers of considerable technological importance for example polyisobutylene PIB polybutenes copolymers obtained from C4 unsaturated hydrocarbons and butyl rubber a random copolymer of isobutylene IB and isoprene. In each group select the alkene most suitable for cationic polymerization.
Provide a mechanism for the formation of a protic initiator from the interaction of boron trifluoride with water. Anethole in a naturally-occuring compound that has been used in cationic. Reaction of Me 3 Si 2 N 2 ZrCH 2 Ph 2 1 with BC 6 F 5 3 gives a cationic benzyl complex which at 25 C expels toluene to afford Me 3 Si 2 Ngraphic omittedSiMe 3η n-PhCH 2-BC 6 F 5 32.
Strong anion coordination to zirconium in cyclometallation product 2 suppresses alkene polymerization whereas the analogous cationic NMe 2 Ph adduct 3 formed by protonolysis of 1. In the current theory of the cationic polymerizations of alkenes the initiation is visualized as the addition of the cationic moiety say R of an initiator to the double bond of the monomer thus generating a carbenium ion at the other end of the double bond and that reaction is replicated by the reaction of the new carbenium ion with more monomer. Cationic Dimerization and Polymerization of Alkenes Some alkenes particularly those with a 3o sp2 C can form dimers two identical molecules condensed into one and polymers many molecules condensed into one when treated with a cationic or radical initiator catalyst.
Cationic polymerization occurs by a chain reaction. Case of an acid-free cationic polymerization of alkenes. An efficient preparation of poly-β-pinene in hexafluoroisopropanol medium.
Ar 173 ___ 005 x 10-3 S. M2- mol-I is close to the value 184 10-35 m2. Mo1-1 which can be Propagation rate constants of the cationic polymerization of alkenes–IIl 1115 Table I.
The polymerization of styrene by 1 in PhNO. At 298 K Exp. 104qmoldm 104xfSm-i 102klsec t -AHpkJ-mol DP DP 37 413 728 6.
