One may also ask which types of cells divide. At the end of cytokinesis two genetically identical daughter cells are produced.

The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell cycleinterphase prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase telophase and cytokinesisto successfully make the new diploid cells.
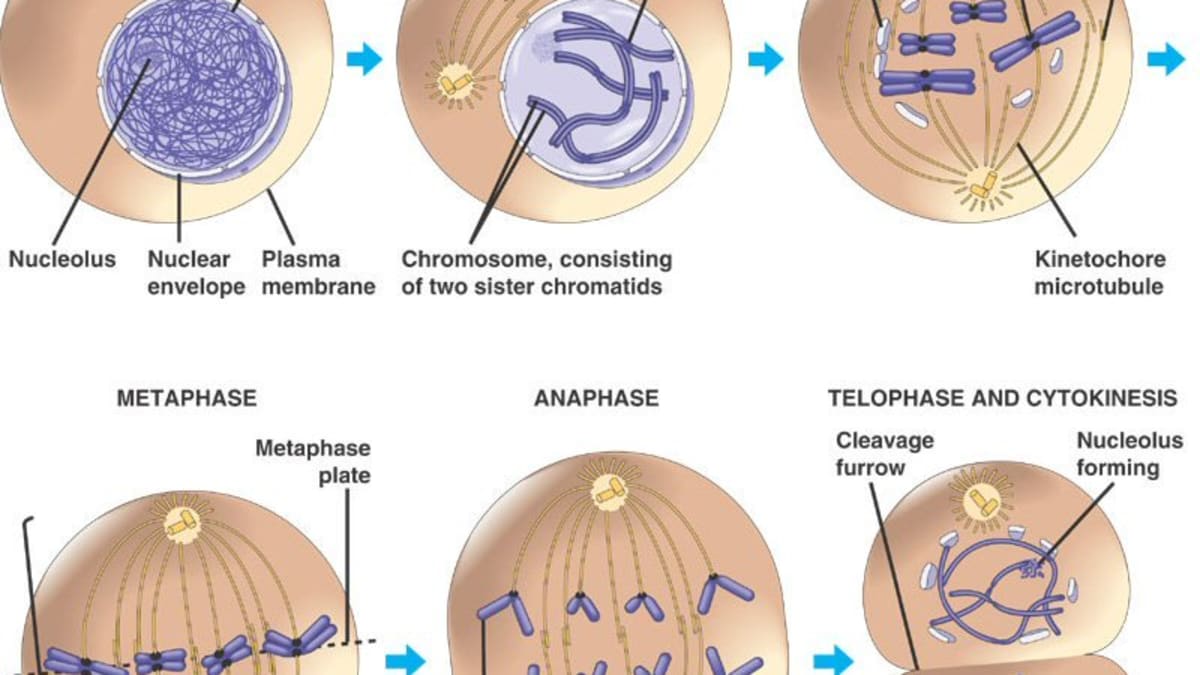
Cell division mitosis and cytokinesis. Cell division in eukaryotic cells includes mitosis in which the nucleus divides and cytokinesis in which the cytoplasm divides and daughter cells form. Mitosis occurs in four phases called prophase metaphase anaphase and telophase. One may also ask which types of cells divide.
There are two types of cell division. During cytokinesis the cytoplasm splits in two and the cell divides as shown below. In animal cells the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cells equator until two daughter cells form.
Thus the goal of mitosis and cytokinesis is now complete because one parent cell has given rise to two daughter cells. Mitosis and cytokinesis occur at the end of the cell cycle as the single cell divides to form two genetically identical copies. The cell cycle can be described in several ways.
Breaking it into G1 S G2 and M phases emphasizes patterns in DNA replication and separation. Cytokinesis is the division of the cells cytoplasm. It begins prior to the end of mitosis in anaphase and completes shortly after telophasemitosis.
At the end of cytokinesis two genetically identical daughter cells are produced. These are diploid cells with each cell containing a full complement of chromosomes. The division of eukaryotic cells occurs in two main stages.
Mitosis is the first stage. Is the process by which the nucleus of the cell is divided into two nuclei each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell. Cytokinesis is the second stage.
Process by which the cytoplasm divides thus forming two. Mitosis division of the nucleus is followed by cytokinesis the division of the cell cytoplasm and the cytoplasmic contents. Cytokinesis overlaps with telophase.
P - chromosome short arm possibly French petit and used along with chromosome and band number to. The two centrosomes are on opposite poles of the cell then cluster at the middle of the cell with their centromeres precisely aligned at the equator of the spindle. Cell division in animals.
Mitosis cytokinesis and the cell cycle. Cell division in animals is a two-step process involving mitosis and cytokinesis and is set up by interphase. Interphase is a growth period for the cell.
In the nucleus the chromosomes are duplicated but are not yet distinguishable because they are still a form of chromatin. These machines segregate chromosomes and divide the cell with high fidelity. Current research on the mechanisms and regulation of spindle morphogenesis chromosome motility and cytokinesis emphasizes how ensembles of dynamic cytoskeletal polymers and multiple motors cooperate to generate the forces that guide the cell through mitosis and cytokinesis.
Completes the division of the cell into two daughter cells. Occurs as a contractile ring of peripheral microfilaments forms at the cleavage furrow and squeezes the cells apart. Actually begins during late anaphase and continues through and beyond telophase.
The mitosis division process has several steps or phases of the cell cycleinterphase prophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase telophase and cytokinesisto successfully make the new diploid cells. The mitosis cell cycle includes several phases that result in two new diploid daughter cells. Cytokinesis is the final stage of cell division during which the cytoplasm splits into two and two daughter cells form.
Karyokinesis or mitosis is divided into five stagesprophase prometaphase metaphase anaphase and telophase. In general mitosis division of the nucleus is preceded by the S stage of interphase during which the DNA is replicated and is often followed by telophase and cytokinesis. Which divides the cytoplasm organelles and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components.
Mitosis and cytokinesis are both part of cell division. While there are several differences between them the two overlap during cell division. Generally mitosis is similar to karyokinesis given that it involves division of the cell nucleus.
In animal cells each centrosome contains a pair of cylindrical centrioles which are themselves composed of complex arrays of microtubules. Centrioles duplicate at a precise time in the cell division cycle usually close to the start of DNA replication. If a cell completed interphase and mitosis but then did not complete cytokinesis the result would be a single cell with two nuclei.
Each nucleus would have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This means that the single binucleate cell would have twice the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Cytokinesis ends the cell division process.
Whether the cell was eukaryotic or prokaryotic these basic events must occur. Cytokinesis is the process where one cell splits off from its sister cell. It usually occurs after cell division.
The Cell Cycle is the sequence of growth DNA replication growth and cell division that all cells go through. MITOSIS CYTOKINESIS AND THE CELL CYCLE - YouTube.
