The two extreme cases of chemical bonds are. The explanation of the attractive forces is a complex area that is described by the laws of quantum electrodynamics.

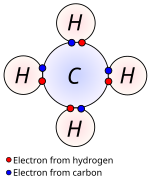
In general strong chemical bonding comes with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms.
Chemical bond chemical bonds. The two extreme cases of chemical bonds are. Bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms. Bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom resulting in positive and negative ions which attract each other.
Other types of bonds include metallic bonds and hydrogen bonding. Chemical bonds are what joins atoms together. Atoms bonded stay together unless the needed amount of energy is transferred to the bond.
In general strong chemical bonding comes with the sharing or transfer of electrons between the participating atoms. The atoms in molecules crystals metals and diatomic gases are held together by chemical bonds. Three types of chemical bonds are met the ionic the covalent and the coordinated bonds.
Once established the coordinated bond acts as a covalent one. Only the covalent and coordinated bonds intervene in absorption and fluorescence. Key Takeaways Chemical bonds.
Chemical bonds are the connections between atoms in a molecule. These bonds include both strong. Chemical bonds are the forces of attraction that tie atoms together.
Bonds are formed when valence. Finally for atoms with the largest. Types of chemical bonds.
Bond length and bond energy Opens a modal Worked example. Interpreting potential energy curves of diatomic molecules Opens a modal Lattice energy Opens a modal Ionic bonds and Coulombs law Opens a modal Practice. Bonds and molecules What is a chemical bond.
A chemical bond is so often represented as a line drawn between atom symbols or a stick connecting two balls in a plastic molecu-lar model that we sometimes tend to think of chemical bonds as things. It is more useful however to regard a chemical bond. Chemical bonding any of the interactions that account for the association of atoms into molecules ions crystals and other stable species that make up the familiar substances of the everyday world.
Chemical Bonding. LIVE Class on Types of Chemical Bonds at 8 PM TodayThere are different types of Chemical Bonds. Ionic or Electrovalent bonds Covalent bo.
Chemical bond plural chemical bonds Any of several attractive forces that serve to bind atoms together to form molecules. See also Thesauruschemical bond. This clip provides an overview of chemical bonds explaining that a chemical bond is not a physical structure but an energy relationship that involves intera.
Chemical bonds form when electrons can be simultaneously close to two or more nuclei but beyond this there is no simple easily understood theory that would not only explain why atoms bind together to form molecules but would also predict the three-dimensional structures of the resulting compounds as well as the energies and other properties of the bonds themselves. See chemical bond chemical bond mechanism whereby atoms combine to form molecules. There is a chemical bond between two atoms or groups of atoms when the forces acting between them are strong enough to lead to the formation of an aggregate with sufficient stability to be regarded as an.
A chemical bond is the physical process responsible for the attractive interactions between atoms and molecules and that which confers stability to diatomic and polyatomic chemical compounds. The explanation of the attractive forces is a complex area that is described by the laws of quantum electrodynamics. Chemical bond refers to the forces holding atoms together to form molecules and solids.
This force is of an electric nature and the attraction between electrons of one atom to the nucleus of another atom contributes to what is known as chemical bonds. Although electrons of one atom repel electrons of another the repulsion is relatively small. Chemical bonds are the attractions between atoms that hold them together to form compounds.
There are three major types of bonding. Covalent bonds that bind together molecular compounds ionic bonds that bind salts and ionic crystals and metallic bonds that bind the atoms of metals. A chemical bond is the physical phenomenon of chemical substances being held together by attraction of atoms to each other through sharing as well as exchanging of electrons.
