
Unicef 2004-2008 data. Prior to 1949 China faced a stark literacy rate of only 15 to 25 percent as well as lacking educational facilities with minimal national curricular goals.
Statistics of China 2014 excluding graduate education institutions Chinas education system is not only immense but diverse.
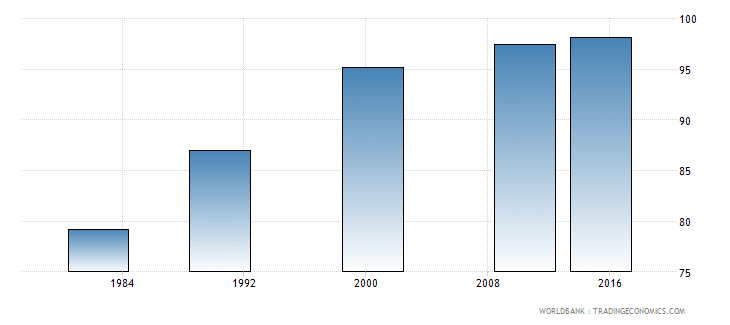
China education literacy rate. 26 rows Literacy Rate Adult literacy rate is the percentage of people ages 15 and above who can both read and write with understanding a short simple statement about their everyday life. China literacy rate for 2018 was 9684 a 172 increase from 2010. The statistic shows the degree of adult literacy in China from 1982 to 2015.
In 2015 the literacy rate which is defined as people aged 15 and above who can read and write had reached about 964. Today Chinese enjoy nine-year free education and the illiteracy rate in China has fallen from over 80 in 1949 to less than 6 percent in 2019. Following are some old photos showing how the Chinese CCP government worked on increasing the literacy rate among the general Chinese population.
By 2008 adult illiteracy rate in China dropped to only 358. Elementary school and junior secondary school enrollment jumped to 995 and 985 respectively. Unicef 2004-2008 data.
When China in 1986 adopted its compulsory education law it set two basic targets. Universal basic education and literacy. The success of this drive can be judged by the fact that the enrollment rate for compulsory education was close to 95 percent in 2018 totaling 15 billion elementary and junior high school pupils nationwide.
Accordingly general enrollment in tertiary education grew to more than 51 percent of the respective age cohorts in 2019. Despite the general improvement of the educational system in China. Statistics of China 2014 excluding graduate education institutions Chinas education system is not only immense but diverse.
Education is state-run with little involvement of private providers in the school sector and increasingly decentralised. County-level governments have primary responsibility of the governing and delivery. 155 rows The literacy rate for all males and females that are at least 15 years old is 863.
Traditional Chinese culture attached great importance to education as a means of enhancing a persons worth and career. In the early 1950s the Chinese communists worked hard to increase the countrys rate of literacy an effort that won them considerable support from the population. By the end of that decade however the government could no longer provide jobs adequate to meet the expectations of those.
At the time China had an illiteracy rate of 80 percent and a population of 467 million people. 1 In 1905 Imperial exams were abolished and the task of educating the worlds largest population began. Progress and Completion in Education.
Progress and Completion in Education. The dropout rate has decreased and the illiteracy rate of young and middle-aged people has declined to less than seven percent. Since the initiation of the reform and opening policies in 1978 marked by the restoration of the higher-education examination system Chinas education got on the road to.
The governments education ministry estimates that 997 percent of Chinas populace has availed of the collective basic education of nine years. This is compulsory education for all of Chinese kids nationwide. Higher education is also important for the Chinese in accordance with the theory of socialist modernization.
China - Literacy rate adult total of people ages 15 and above Definition. Adult literacy rate is the percentage of people ages 15 and above who can both read and write with understanding a short simple statement about their everyday life. School enrollment Primary net.
Net enrollment ratio is the ratio of children of official school age based on the International Standard Classification of Education 1997 who are enrolled in school to the population of the corresponding official school age. Primary education provides children with basic reading writing and mathematics skills along with an elementary understanding of such subjects as. Economic development assumed Chinas rate of literacy to be low and then used it to explain Chinas poor performance.
Using new research materials and a more. With the communist victory and the establishment of the Peoples Republic of China the party begins an educational campaign dedicated to expanding the nations literate and educated masses. Prior to 1949 China faced a stark literacy rate of only 15 to 25 percent as well as lacking educational facilities with minimal national curricular goals.
