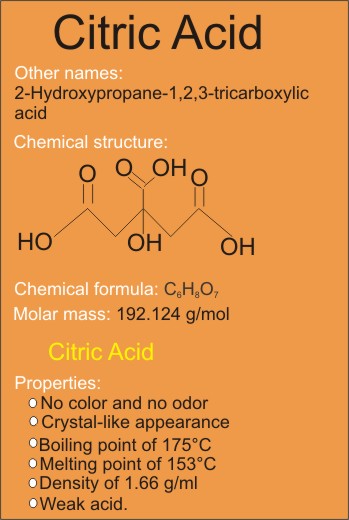
C 6 H 8 O 7 CH 2 COOH-COHCOOH-CH 2 COOH Molecular mass. 0015 mmHg at 25C Enthalpy of Vaporization.
This means that when citric acid is.
Citric acid boiling point. Citric acid is not expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces SRC based upon a vapor pressure of 166X10-8 mm Hg at 25 C 5. Citric acid reached 53 of its theoretical BOD in 5 days using a sludge inoculum 6 suggesting that biodegradation may be an important environmental fate. 3074 Fahrenheit Boiling Point.
According to the University of Wisconsin-Madison the boiling point of citric acid and its decomposition temperature is the same. This means that when citric acid is. Citric acid decomposes with loss of carbon dioxide above about 175 C.
Soluble in Water 1174gL at 10C 1809gL at 30C 3825gL at 80C. Citric acid also dissolves in absolute anhydrous ethanol 76 parts of citric acid per 100 parts of ethanol at 15 C. 3096420 C at 760 mmHg Vapour Pressure.
0015 mmHg at 25C Enthalpy of Vaporization. 63860 kJmol Flash Point. 1552244 C Index of Refraction.
Not flammable Evaporation rate n-BuAc1. 16 mmHG Vapor density air 1. 062 Relative density specific gravity.
124 at 20C Solubility in water. Citric acid meets analytical specification of Ph. Eur BP USP E330 anhydrous 995-1005 based on anhydrous substance 791725 Citric acid anhydrous free.
Page 1 o f 7 MSDS - Citric Acid Material Safety Data Sheet MSDS - Citric acid 1Chemical Product and Company Identification. 153C 3074F Critical Temperature. Page 5 o f 7 MSDS - Citric Acid Specific Gravity.
1665 Water 1. 6 rows Citric Acid. Freezing Point 19 F.
Boiling Point 220 F. A solution of citric acid C6H8O7 in 50 g of acetic acid has a boiling point elevation of 176 K. If Kb for acetic acid is 307 K kg mol-1 what is the molality of solution.
Melting Point Approx153 C at 1013 hPa Boiling pointboiling range C. Citric acid monohydrate reagent grade 98 GCtitration Citric acid monohydrate 995 suitable for amino acid analysis. Citric acid monohydrate European Pharmacopoeia EP Reference Standard.
Citric acid monohydrate pa ACS reagent reag. 157 degrees celcius Citric acid is found in vegetables and fruits especially citric fruits like oranges lemons limes and grapefruits. Up to 8 of the dry weight of lemons and limes can be citric acid.
Citric acid was first obtained by Scheele when he crystallized it from lemon juice. Wehmer found that penicillium. Chemically citric acid shares the properties of other carboxylic acids.
When heated above 175 ÂC it decomposes through the loss of carbon dioxide and water. Lemons and other citrus fruit contain a great deal of citric acid. Citric acid can be esterified at one or more of its three carboxylic acid groups to form any of a variety of mono- di- tri- and mixed esters.
More than 50 of Citric Acid production used as an acidity regulator in beverages some 20 in other food applications 20 for detergent applications and 10 for applications other than food such. Decomposes above 175C. The solution in water is a medium strong acid.
Reacts with oxidants and bases. C 6 H 8 O 7 CH 2 COOH-COHCOOH-CH 2 COOH Molecular mass. 1921 Decomposes at 175C Melting point.
153C Solubility in water g100ml at 20C. 100C Explosive limits vol in air. Citric acid trisodium salt dihydrate Trisodium citrate dihydrate Linear Formula.
HOCCOONaCH 2 COONa 2 2H 2 O. Citric acid is easily crystallized from its solution. These crystals appear as a white powder.
The boiling point of citric acid is about 310 o C. Citric acid is miscible in water and in anhydrous ethanol. Due to the presence of carboxylic groups citric acid is capable of forming strong hydrogen bonds.
