Definition of Remote Sensing. Remote sensing is the examination of an area from a significant distance.
Remote sensing can be defined as the collection of data about an object from a distance.
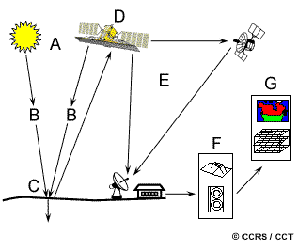
Define remote sensing in geography. Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance typically from satellite or aircraft. Special cameras collect remotely sensed images which help researchers sense things about the Earth. Remote sensing is any method of collecting data about an object or location without making physical contact with it.
For example you can fly a satellite or aircraft over an area and use that to. Remote Sensing can be defined as the science and art of acquiring information about an object made from a distance without physical contact with the object. In practice remote sensing is the utilization at a distance as from aircraft spacecraft satellite or ship of any device for gathering information about the environment.
Introduction to Remote Sensing. Remote sensing in the science and art of obtaining information about an object area or phenomenon through the analysis of data acquired by a device that is not in contact with the object area or phenomenon under investigation. It is a technology for sampling electromagnetic radiation to acquire and interpret non-immediate geospatial.
Remote sensing is the art and science of making measurements of the earth using sensors on airplanes or satellites. Definition of Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing can be defined as the science and art of acquiring information about an object made from a.
However modern Remote Sensing means acquiring information about earths land and water surfaces by using reflected or emitted electromagnetic energy. From the following definitions we can have a better understanding about Remote Sensing. According to White 1977 Remote Sensing includes all methods of obtaining pictures or other.
Click here to get an answer to your question Definition of remote sensing in geography devanandshilpa1143 devanandshilpa1143 12112017 Social Sciences Secondary School answered Definition of remote sensing in geography 2 See answers. Remote sensing involves the use of extracting information about a geographic area through the use of aerial or satellite imagery. Remote sensing is the act of observing geographic features or phenomenon from a distance.
Remote sensing can be defined as the collection of data about an object from a distance. Humans and many other types of animals accomplish this task with aid of eyes or by the sense of smell or hearing. Geographers use the technique of remote sensing to monitor or measure phenomena found in the Earths.
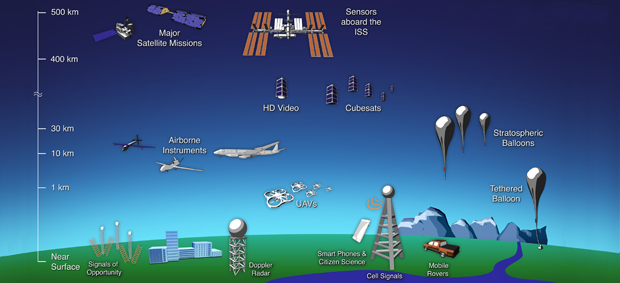
Remote sensing is a type of geospatial technology that samples emitted and reflected electromagnetic EM radiation from the Earths terrestrial atmospheric and aquatic ecosystems in order to detect and monitor the physical characteristics of an area without making physical contact. The hypothesis tested in this study was that remote sensing constitutes a particular case of an arbitrary uniform spatial sampling grid used to obtain measurements about geographical entities that induces the scale and aggregation effect responsible for haphazard analysis results. The main objective was to evaluate the impact of measurement scale and spatial aggregation on the information.
Admission to the Remote Sensing geoInformation and Visualization masters degree program requires a qualifying university degree in the field of the geosciences geography physics mathematics biology environmental sciences information science or a similar program of study with a standard period of study of at least three years and a total share of at least 36 credit points CP in the. It is a surveying and data collection technique. Remote sensing is a technique used to survey and collect data regarding an object or a phenomenon without any physical contact with the object or the phenomenon being observed.
In remote sensing ground truth refers to information collected on location. Ground truth allows image data to be related to real features and materials on the ground. The collection of ground truth data enables calibration of remote-sensing data and aids in the interpretation and analysis of.
Remote sensing is the examination of an area from a significant distance. It is used to gather information and imaging remotely. This practice can be done using devices such as cameras placed on the ground ships aircraft satellites or even spacecraft.
Today data obtained through remote sensing is usually stored and manipulated with computers.