
1 Mix 08 ml Substrat and 02 ml enzyme 2 Incubate for 10 min 3 Add 1 ml DNSA 4 Boil for 5 min and the cool down 5 Add 9 ml Water 6 Fill 15 ml in a cuvette and measure Absorption at 540 nm. The procedure is the following.
5 in comparision with p-DMAB method boric acid method and DNS assay.
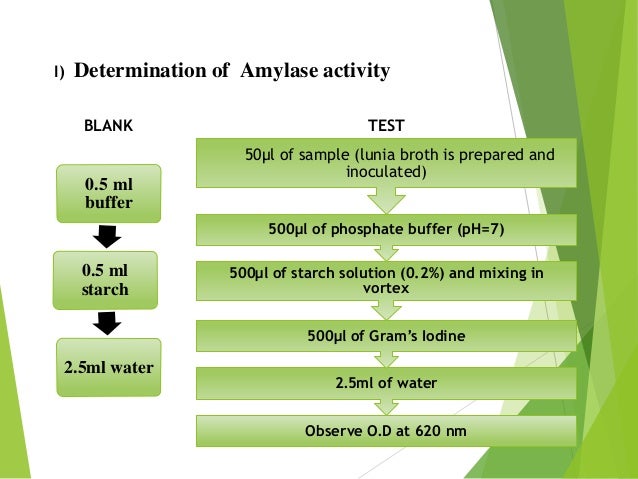
Dns method for enzyme assay. Generally different methods are followed for the enzyme assays. The dinitro salicylate DNS method detects the reducing sugars liberated by the action of hydrolase enzymes on carbohydrates under specific pH and temperatures Bailey 1988. Based on the source of enzyme the pH and temperature of enzyme assay parameter vary.
The procedure is the following. 1 Mix 08 ml Substrat and 02 ml enzyme 2 Incubate for 10 min 3 Add 1 ml DNSA 4 Boil for 5 min and the cool down 5 Add 9 ml Water 6 Fill 15 ml in a cuvette and measure Absorption at 540 nm. DNSA is more sensitive and easier to use than Benedicts reagent.
Used with a colorimeter it is ideal for measuring the action of enzymes such as invertase cellulase and amylase where reducing sugars are produced. Thus it helps to meet two of the important practical requirements of the current English biology specifications. The procedure is the following.
1 Mix 08 ml Substrat and 02 ml enzyme 2 Incubate for 10 min 3 Add 1 ml DNSA 4 Boil for 5 min and the cool down 5 Add 9 ml Water 6 Fill 15 ml in a cuvette and measure Absorption at 540 nm. As we know DNS is an internationally acceptable method for xylanase enyzme activity assay. It has been use as a method to calculate the enzyme activity of xylanase by measuring the reducing sugar.
Methods of quantitatively following enzyme reaction. Using a fluorometer. NAD and NADP do not fluoresencein their oxidized forms but the reduced form have a blue fluorescence reduction reaction.
3- Sampling methods. By withdrawing samples at intervals and. Method of Enzyme Assay Enzyme activity is measured in vitro under conditions that often do not closely resemble those in vivo.
The objective of measuring enzyme activity is normally to determine the amount of enzyme present under defined conditions so that activity can be compared between one sample and another and between one. The use of enzyme assays especially coupled assays allows for the rapid and in some cases continuous analysis of MD perfusate with very low detection limits and without the need for a separation step imparted by the high specificity of the enzyme. To date most MD-coupled enzyme assays employ nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD-dependent enzymes and produce.
The procedure is the following. 1 Mix 08 ml Substrat and 02 ml enzyme 2 Incubate for 10 min 3 Add 1 ml DNSA 4 Boil for 5 min and the cool down 5 Add 9 ml Water 6 Fill 15 ml in a cuvette and measure Absorption at 540 nm. For measuring Hemicellulase activity Xylanase assay I used the procedure adapted from Bailey et al.
1992 using the Xylan as the substrate 1ml DNS reagent 3ml and 01Mcitrate phosphate. Method a modification were made in method of incubation time of substrate and enzyme but still chitinase activity obtained were less about 132 Uml Fig. 5 in comparision with p-DMAB method boric acid method and DNS assay.
All the four methods used in this research has an advantage of. The ChitO-based assay has clear advantages for the detection of chitinase and cellulase activity over the conventional Schales procedure and DNS method. The detection limit is lower and there is no requirement for harsh conditions for the development of the signal.
The assay also involves fewer and easier handling steps. There is no need for boiling to develop the color and results are. Our invertase assay uses a yellow reagent called DNS 439 mM 35-dinitrosalicylic acid and 250mM NaOH that changes to an amber color in the presence of reducing sugars such as glucose and fructose.
Reducing sugars can act as mild reducing agents due to an aldehyde group. Because sucrose is not a reducing sugar the activity of the invertase enzyme can be. A heterogeneous enzyme immunoassay method is also called enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ELISA.
In this type of assay one of the immunochemical reaction components antigen or antibody is first non-specifically adsorbed to the surface of a solid phase. Tubes wells of microtiter plates and magnetic particles may be used as the solid phases. The solid phase facilitates separation of bound- and free-labelled reactants.
A homogeneous enzyme. IB Biology IA starch hydrolysis enzyme amylase glucose assay with DNS. These data suggest then that the DNS assay can be used as an accurate analytical method for the evaluation of reducing sugars both in pure solution as well as in superna- tants from enzymatic saccharifications of purified cellulo- sics if glucose is the sole product.
However only specific assay methods such as HPLC and YSI-type glucose ana-.
