From the observed extreme diversity of antibody molecules we are tempted to think that any antigen can find its specific binding receptors ie its preexisting antibody molecules. Protein antigens are called.

We hear a lot about the production of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 but not all B cells go on to produce antibodies and of those that do some produce a different type of antibodies than others.
Do b cells produce antibodies. B Cells Make Antibodies as Both Cell-Surface Receptors and Secreted Molecules As predicted by the clonal selection theory all antibody molecules made by an individual B cell have the same antigen-binding site. The first antibodies made by a newly formed B cell are not secreted. One of the major roles that B cells play in an immune response is the production of antibodies that specifically recognise and bind to proteins on the invading bacteria or virus particles.
The binding of specific antibody to its target can prevent viruses from entering cells or aid phagocytes in identifying and destroying the bacteria or viruses. Key Concepts and Summary B lymphocytes or B cells produce antibodies involved in humoral immunity. B cells are produced in the bone marrow where.
B-cell receptors BCRs are membrane-bound monomeric forms of IgD and IgM that bind specific antigen epitopes with their. Protein antigens are called. We hear a lot about the production of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 but not all B cells go on to produce antibodies and of those that do some produce a different type of antibodies than others.
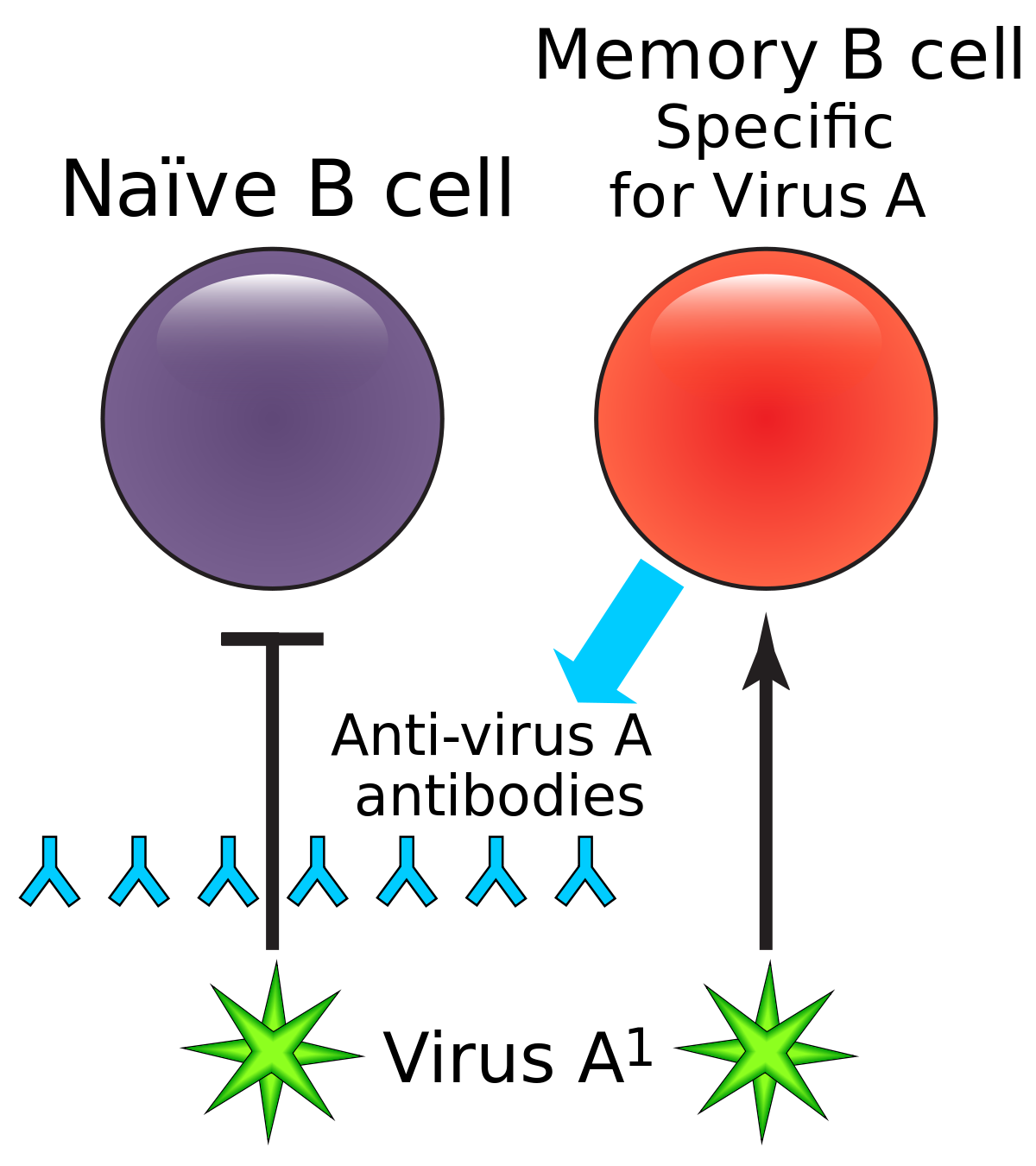
Making good antibodies without making potentially harmful ones is the goal of vaccines but do we know how to tell the difference easily. In this webinar Professor Dunn-Walters provided us with a summary. Antibodies are produced only by B lymphocytes.
Humoral immune responses are initiated by binding of antigen to membrane bound antibody on B cells. Activated B cells secrete soluble antibodies of the same specificity as the membrane receptors. Antibody responses are specialized and enhanced by signals from helper T cells.
One of our defense systems most important strategies involves B lymphocytes also known as B cells which produce antibodies that target and neutralize pathogens. B cells play a. B-cells fight bacteria and viruses by making Y-shaped proteins called antibodies which are specific to each pathogen and are able to lock onto the surface of an invading cell and mark it for destruction by other immune cells.
B-lymphocytes and cancer have what may be described as a love-hate relationship. For example B-cells sometimes inhibit tumor development by producing antibodies. B cells have antibodies on their cell surface that allow them to recognize anything foreign.
When they encounter a pathogen the B cells transform into plasma cells which start producing. Antibodies are produced by specialized white blood cells called B lymphocytes or B cells. When an antigen binds to the B-cell surface it stimulates the B cell to divide and mature into a group of identical cells called a clone.
The mature B cells called plasma cells secrete millions of antibodies into the bloodstream and lymphatic system. The immune system mounts several types of attacks against invading viruses including the production of antibodies Ab to neutralize the virus B-cells that ramp up antibody production and CD4 and CD8 T-cells to kill virus-infected cells. In coronaviruses like the COVID-19 virus T-cells seem to produce the most lasting protection against infection.
Image courtesy of Marc Hellerstein. B cells and antibodies are only part of the immune response. T cells help B cells produce antibodies which are proteins that can bind to a specific pathogen and.
Computer illustration of plasma cells B-cells orange secreting antibodies white against viruses blue Juan Gaertner Science Photo Library. Antibodies are Y-shaped. B cells have antibodies on their cell surface that allow them to recognize anything foreign.
When they encounter a pathogen the B cells transform into plasma cells which start producing. For B lymphocytes we know that these antigen binding structures are immunoglobulin Ig molecules antibodies. One B cell makes one of the many Ig molecules and displays them in many copies on the surface membrane.
From the observed extreme diversity of antibody molecules we are tempted to think that any antigen can find its specific binding receptors ie its preexisting antibody molecules. Essential problems of how to produce large quantities of such antigen-specific antibodies. B cells are white blood cells that develop to produce antibodies.
These antibodies or immunoglobulins can bind to harmful foreign particles such as. B-lymphocytes are defensive white blood cells. They produce antibodies that attack the antigens left behind by the macrophages.
T-lymphocytes are another type of defensive white blood cell. They attack cells in the body that have already been infected.