The risk of flooding such as coastal erosion increases in sea level land development and reductions in the capac-ity of river channels. Soil becomes saturated after prolonged rainfall.
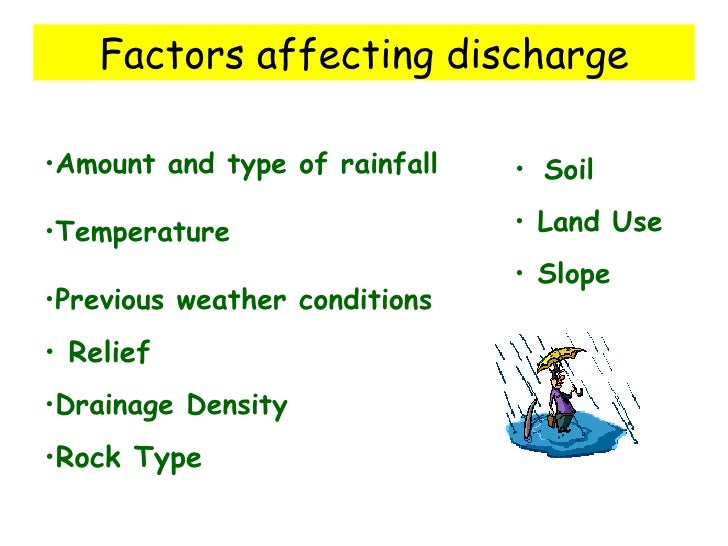
Factors affecting flood risk.
Factors affecting flood risk. Factors affecting flood risk. Attempts at flood prediction. Flood mitigation case studies.
Agricultural activities and water quality. Pressures on lakes and aquifers. Internationally shared water and conflict.
Participation of local communities. There are a range of physical factors that can lead to flooding. Soil becomes saturated after prolonged rainfall.
This leads to an increase in surface run-off as rainfall can no longer infiltrate the soil. This leads to more water entering the river channel increasing the likelihood of. A flood can be defined when the amount o.
In this video from OMG Revision we will be looking at the physical and human factors that can affect the flood risk. 1Finally a flood hazardis the potential for inundation that involves risk to life health property and natural floodplain resources and functions. It is comprised of three elements.
Severity magnitude duration and extent of flooding probability of occurrence and speed of onset of flooding. Urbanisation leads to water being transferred rapidly over impermeable concrete. Water travels faster over steep slopes in mountainous areas leading to greater flood risk.
Deforestation leads to land no longer being protected from rainfall increasing the transfer of water into river channels. Among the various factors that contribute to flood risk heavy storms inadequate storm drainage systems and the concentration of population and assets. Intensive rainfall and high melting of snow are two main causes of flood.
As melting of the the worlds glaciers occurs due to warmer global temperatures sea level rise is occurring around the world also leading to an increased risk of flooding in low-lying coastal regions and in heavily urbanized floodplains such as. The common health impacts of flooding are complex 13 they include. Causing acute stress 14 malaria and cholera 15 depression 16 17 anxiety and posttraumatic stress disorder PSTD damage to infrastructure 18 the loss of the existing health system and healthcare delivery services 19 damage to water and sewage systems and disruption to existing public health care.
However poverty and limited access to financial resources are the major constraints affecting the adaptive capacity to combat future flooding events. For farmers whose farms are located in vulnerable areas and who have limited financial resource an implementation of non-structural techniques such as changing crop patterns and altering harvest seasons should be promoted. Urbanisation can cause flooding because many of the surfaces in towns and cities are Impermeable.
Deforestation the removal of trees can increase soil erosion reduce interception and increase flood risk. Increases in population density can also have an. This video addresses the primary factors that influence the timing volume and duration of flood events.
The risk of flooding such as coastal erosion increases in sea level land development and reductions in the capac-ity of river channels. In addition evidence suggests that climate change has increased the risk of flooding from rivers and perhaps also from coastal storms making FEMAs models of flood frequencies out of date.
