
Progressive taxes increase proportionately to income so those who make more pay both a larger absolute amount of taxes and a. Macpherson Abstract This paper examines the extant literature on horizontal and vertical inequity in the taxation of real property.
Those decisions of the Germany Constitutional Court require parity horizontal equity – among taxpayers and suggest but do not require progressivity in taxation vertical equity.
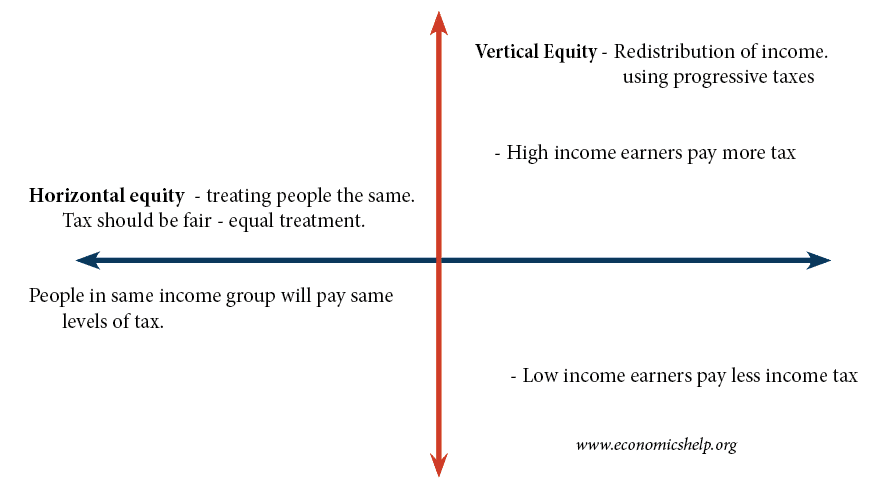
Horizontal and vertical equity in taxation. Horizontal equity is based on the idea that those who have the same amount of wealth or similar levels of income should be taxed at the same rate as others within that same income. Horizontal equity also requires a tax system which doesnt give preferential treatment to certain individualscompanies. Vertical equity Vertical equity is concerned with redistributing income within society.
It implies that people with higher incomes should pay more tax. Vertical equity requires proportional or progressive taxes. For example income tax helps improve vertical equity by taxing.
Horizontal and Vertical Equity in Taxation as Constitutional Principles. Germany and the United States Contrasted Florida Tax Review Vol. 259-334 2006 61 Pages Posted.
21 Sep 2008 Last revised. Horizontal and Vertical Equity in Taxation as Constitutional Principles. Germany and the United States Contrasted by Henry Ordower Professor of Law and Co-Director Center for International and Comparative Law Saint Louis University School of Law AB.
Washington University MA JD. The University of Chicago. Horizontal equity is a tax principle whereby equals are treated as equals hence individuals with the same income should pay an equal amount of tax.
On the other hand vertical equity is a method of tax collection based on the income amount whereby taxes paid increase with an increase in income. Both horizontal and vertical equity are affected by the way income is taxed. Taxe rates can be progressive regressive or proportional.
Progressive taxes increase proportionately to income so those who make more pay both a larger absolute amount of taxes and a. Horizontal and Vertical Inequity in Real Property Taxation G. Stacy Sirmans Dean H.
Gatzlaff and David A. Macpherson Abstract This paper examines the extant literature on horizontal and vertical inequity in the taxation of real property. Some major conclusions from the literature are.
A horizontal inequity may occur from unequal. In this recent literature the term vertical equity refers to any compari- son of the after-tax income distributions generated by tax systems. Meas- ures of vertical equity or inequity are essentially measures of after-tax in- come inequality.
The term horizontal equity in this literature refers to the. According to the concept of horizontal equity equals should be treated equally that is persons with the same ability to pay should be made to bear the same amount of tax burden. According to the vertical equity unequals should be treated unequally that is how the tax burden among people with different abilities to pay is divided.
Vertical equity and economic efficiency. It is important to emphasize that horizontal equity is concerned with individuals who are similarly situated not with those who are identically situated Tautologically any conceivable tax arrangement will treat identically situated taxpayers equally. This paper examines the extant literature on horizontal and vertical inequity in the taxation of real property.
Some major conclusions from the literature are. A horizontal inequity may occur. The Principle of Horizontal and Vertical Equity Horizontal equity and vertical equity are relevant to investing because they often influence taxation policies.
The concepts of horizontal equity and vertical equity date back to the works of Aristotle and Plato. They have become increasingly relevant in. As with a non-discriminatory tax system equity into health resources is divided into horizontal and vertical dimensions.
In vertical equity social members with different levels of needs can receive different amounts of health resources appropriately. Those decisions of the Germany Constitutional Court require parity horizontal equity – among taxpayers and suggest but do not require progressivity in taxation vertical equity. Horizontal equity is the principle that taxpayers with equal income should pay equal tax.
Vertical equity requires that tax obligations vary in proportion to income such that if A has a greater income than B A will owe more income tax than B. Scholars ranging from the. Horizontal equity is an economic theory that states that individuals with similar income and assets should pay the same amount in taxes.
Horizontal equity should apply to individuals considered. Vertical equity is a method of income taxation whereby more taxes are paid as income increases. Vertical equity is based on the principle of ability to pay through progressive tax rates or.
Horizontal and vertical equity are two different concepts but can work together in the same tax system with the aim of creating better equity overall.