
CAG at least 10 diseases Huntington disease spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy and seven SCAs CGG fragile X fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome other fragile sites GCC CCG CTG myotonic dystrophy type 1 Huntington disease-like 2 spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 Fuchs corneal. The repeats may cause a loss in gene function as in Fragile X or may result in the gain of a new abnormal protein and thus a new function as in myotonic dystrophy and Huntington disease.
The Genetic Testing Registry GTR provides information about the labs that offer genetic testing for fragile X syndrome.
How are fragile x syndrome and huntington disease similar. How are Fragile X syndrome and Huntington disease similar A Both exhibit a late How are fragile x syndrome and huntington disease School American University of Beirut. The repeats may cause a loss in gene function as in Fragile X or may result in the gain of a new abnormal protein and thus a new function as in myotonic dystrophy and Huntington disease. Although a variety of trinucleotide repeat diseases have been reported and merit consideration this discussion will focus primarily on Fragile X syndrome myotonic dystrophy and Huntington disease.
Other microsatellites are located in regulatory flanking or intronic regions of genes or directly in codons of genes microsatellite mutations in such cases can lead to phenotypic changes and diseases notably in triplet expansion diseases such as fragile X syndrome and Huntingtons disease. Similar modelling has been published for the Huntingtons disease data. However in this paper we demonstrate that a uniform approach works for fragile X and Huntingtons disease although the detailed assumptions of the model have to be different.
These difference provide insight into the mechanisms of expansion in both cases. Fragile X syndrome often looks very similar to Autism Spectrum Disorder ASD. Developmental delay cognitive impairment stereotypic repetitive without function behaviors such as hand flapping and body rocking and gaze avoidance are features present both in individuals with autism and individuals with fragile X syndrome.
Myotonic dystrophy DM Huntingtons disease HD and Fragile X syndrome FRAXA are three monogenic disease which are caused by so-called dynamic mutations. These mutations are caused by triplet repeats inside or in the vicinity of the gene which have the tendency to expand beyond the normal range thus disrupting the normal functioning of the gene. The researchers are now looking for similar RNA-DNA duplexes in other trinucleotide repeat diseases including Huntingtons disease a degenerative brain disease myotonic dystrophy 1 and 2.
Fragile X syndrome also known as Martin-Bell syndrome is a sex-linked genetic disorder. The exact frequency of Fragile X syndrome is unclear but the CDC estimates that roughly 14 in 10000 males and 09 in 10000 females are affected by this disorder. Males afflicted with this syndrome typically have a moderate to severe form of intellectual handicap.
Fragile X-Associated TremorAtaxia Syndrome FXTAS is a disorder of the nervous system that can cause tremors and problems with walking balance also called ataxia memory and mood disorders among older adults. FXTAS can be caused by a premutation in. Fragile X syndrome has been found in all major ethnic groups and races and is caused by an abnormality mutation in the FMR1 gene.
FMR1 is a gene located on the X chromosome that produces a protein called FMRP needed for proper cell function. The syndrome became known as the fragile X syndrome because some individuals with the disorder were found to have a segment of their X chromosome that appeared to be broken or fragile. Carrier testing for at-risk relatives and prenatal testing for pregnancies at increased risk are possible if the diagnosis of an FMR1-related disorder including fragile X syndrome has been confirmed in a family member.
The Genetic Testing Registry GTR provides information about the labs that offer genetic testing for fragile X syndrome. The intended audience for the GTR is health care providers. Fragile X Syndrome FXS often occurs with other conditions.
Learn about some of these conditions. Fragile X Syndrome Related Concerns. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
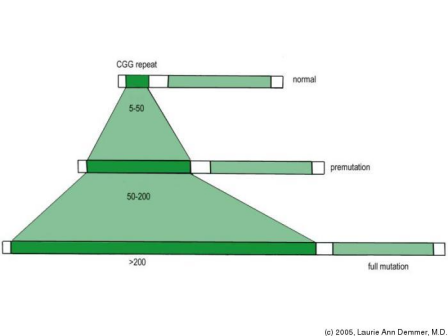
The fragile X mental retardation 1 gene FMR1-related disorder fragile X syndrome FXS is the most common heritable form of cognitive impairment and the second most common cause of comorbid autism. FXS usually results when a premutation trinucleotide CGG repeat in the 5 untranslated region of the FMR1 gene CGG 55-200 expands over generations to a full mutation allele CGG 200. Boys are more likely to have fragile X than girls and they have more severe symptoms.
This is because girls have two copies of the X chromosome. Even if one X chromosome has the gene change the. The leading theory of fragile X holds that when FMRP is missing protein synthesis can run rampant and disrupt cognitive processes.
A study published last month however has complicated scientists understanding of the syndrome. It hints that loss of FMRP instead causes a dearth of proteins. What is the fragile X syndrome premutation.
CAG at least 10 diseases Huntington disease spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy and seven SCAs CGG fragile X fragile X tremor ataxia syndrome other fragile sites GCC CCG CTG myotonic dystrophy type 1 Huntington disease-like 2 spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 Fuchs corneal. These mechanisms link the fragile X mutation to the profound intellectual deficits in fragile X syndrome Zhao says. By blocking the proper formation and function of mitochondria the fragile X mutation may also play a role in several other conditions.
About 2 to 3 percent of people with autism have fragile X syndrome.