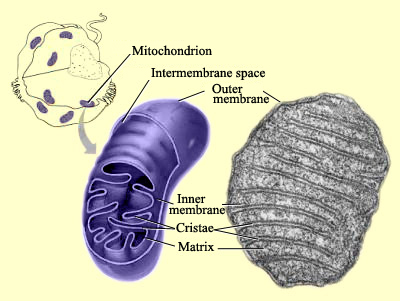
A when a protoeukaryote engaged in a symbiotic relationship with a protocell b from infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions. The endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts suggests that mitochondria are descended from specialized bacteria probably purple nonsulfur bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another species of prokaryote or some other cell type and became incorporated into the cytoplasm.

In other words she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an unbroken line purely through their mothers and through the mothers of those mothers back until all lines converge on one woman.
How did mitochondria originate. The endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts suggests that mitochondria are descended from specialized bacteria probably purple nonsulfur bacteria that somehow survived endocytosis by another species of prokaryote or some other cell type and became incorporated into the cytoplasm. These similarities have prompted the hypothesis that mitochondria are derived from bacteria by a process termed endosymbiosis. The first person to recognize mitochondria as descendants of endosymbiotic bacteria was Ivan Wallin in 1926 1.
After this the theory fell out of grace possibly due to the college textbook of EB. Wilson who regarded endosymbiotic theories as too fanciful. A popular theory among evolutionary biologists for the origin of mitochondria is that they were once free-living organisms that became incorporated into cells.
However from what we know of genetics any free-living organism would probably need at least 256 genes and at least about 300000 base pairs of DNA. All free-living organisms today have. As vestiges of their ancient origin mitochondria still have their own genome although some of their DNA has been transferred to our genome.
Biology 24102019 0100 twhalon72 According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells how did mitochondria originate. A when a protoeukaryote engaged in a symbiotic relationship with a protocell b from infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions. According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells how did mitochondria originate.
A when a protoeukaryote engaged in a symbiotic relationship with a protocell b from infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions c from the nuclear envelope folding outward. According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells how did mitochondria originate. From engulfed originally free-living proteobacteria.
According to the endosymbiosis hypothesis also referred to as the endosymbiosis theory how did mitochondria originate. They were direct results of genetic mutations in eukaryotic cells that allowed for oxygen-using metabolism. They were eukaryotes that became engulfed by a progenote.
They were prokaryotes that became engulfed by urkaryotes. According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells how did mitochondria originate. A from infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions.
Mitochondria are thought to be derived from aerobic bacteria that became part of the eukaryotic cell through endosymbiosis. Asked Sep 8 2019 in Business by HalaMadrid management. New mitochondria originate by the division of pre-existing mitochondria.
It has been observed that sometimes mitochondria become elongated and broken into small pieces. Each piece forms a new mitochondrion in later stages. During cell division mitochondrion divides transversely into two and each develops into a mature mitochondrion later on.
In human genetics the Mitochondrial Eve also mt-Eve mt-MRCA is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor MRCA of all living humans. In other words she is defined as the most recent woman from whom all living humans descend in an unbroken line purely through their mothers and through the mothers of those mothers back until all lines converge on one woman. Based on the serial endosymbiotic theory how did mitochondria originate.
From the nuclear envelope folding outward and forming mitochondrial membranes from engulfed originally free-living prokaryotes from infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for oxygen-using metabolism when an early eukaryote became a parasite within a protobiont by tertiary endosymbiosis. How did mitochondria originate. Asked by Wiki User.
Wiki User Answered 2014-03-30 062026. They were originated from bacteriaSymbiotic living turned them into. According to the endosymbiosis theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells how did mitochondria originate.
By secondary endosymbiosis Bfrom the nuclear envelope folding outward and forming mitochondrial membranes Cfrom infoldings of the plasma membrane coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions. Mitochondria are thought to originate from symbiotic prokaryote. And they reside outside the nucleus.
Egg only the egg provides the mitochondria of the future fetus. During growth of the organism.