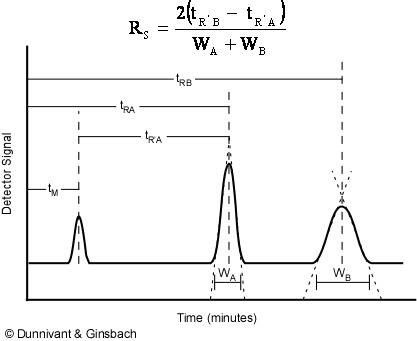
As the chromatograph separates and measures each compound it records the detector response to each one calculating. Additionally gas chromatography can be used to determine vapor pressure heat of solution and.
The repeatability of peak area is.
How to calculate concentration from gas chromatography. Inject known concentrations of the gas say 99 50 10 and obtain the peak areas for this concentration. Plot a calibration graph ie. Concentrations versus corresponding peak areas.
The concentration is calculated by comparing the peak area of the analyte in the sample with the peak area of the standard of a known concentration. If you have used an internal standard you will. These detector response factors are determined by passing a mixture of known species proportions a calibration gas sample through the chromatograph while programming the chromatograph computer with the known concentrations of this calibration gas.
As the chromatograph separates and measures each compound it records the detector response to each one calculating. If then your sample has a area of 600 AU you know it has a concentration of 001 600 645 mgmL. These types of calculations assume that the response factor between your standard and sample is 11 ie.
1 AU is 001 mgmL for both compounds this is not always the case. If all goes well you will see a linear relationship. The slope of the best-fit straight line is the response factor RF.
Now run your samples. Divide the peak area by the response factor to determine concentration. Concentration of target component in unknown sample 100 ppm concentration of internal standard in unknown sample 07 12 58 ppm Component A concentration is 58 PPM 345.
Calculate the total area in cm2 of all peaks by adding the corrected areas. Record the total area in the space provided in the Calculation Table 3. CALCULATION TABLE 3 Peak Peak Identification Total Peak Area same value for all Percent Composition 4.
Calculate the mass percent for each component of your mixture. Im fairly new to chromatography so just wanted to check that the following equation is correct. Im doing gas chromatography and using an internal standard IS to calculate the concentration of an unknown based on that.
The equation I have found is. Of Unknown Analyte Peak Area of Analyte Peak Area of IS x Concentration of IS. Quickly determine column dimensions and easily convert between flow rates linear velocity and residence time.
Get the recommended compression factor as well as the minimum resin volume required to pack a column easily. This tool also provides you with catalogue numbers and links of our comprehensive chromatography media portfolio at your fingertips. The area of a peak is proportional to amount of the compound that is present.
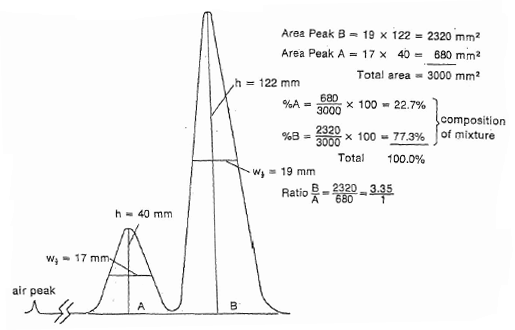
The area can be approximated by treating the peak as a triangle. The area of a triangle is calculated by multiplying the height of the peak times its width at half height. Calculation of results From the area measurements using simple arithmetic it is simple to calculate the concentration of each component as a percent of the total.
A LatexfracArea of Peak A X 100Total Areas of Peaks A B C Dlatex Real Chromatogram. Uses of Gas Chromatography. GC is used as one test to help identify components of a liquid mixture and determine their relative concentration.
It may also be used to separate and purify components of a mixture. Additionally gas chromatography can be used to determine vapor pressure heat of solution and. Three factors determine how we introduce a sample to the gas chromatograph.
First all of the samples constituents must be volatile. Second the analytes must be present at an appropriate concentration. Introduction to basic organic laboratory equipment and techniqueshttpwwwncsueduchemistry.
Theoretically GC can be used to determine the components of a sample because under fixed temperatures and carrier gas flow rates the retention time of a substance should be the same. It should be noted that the retention time of a substance may not be unique to just that substance which is why GC is often paired with Mass Spectroscopy to give concrete results. The chromatogram obtained from the unknown sample looks.
This method is used to determine changes in concentration of a known sample. In the sample matrix can mitigate the effect matrix effect of changes in sample composition when introduced to a gas chromatograph. DisadvantagesExtra work is required to add the target component.
This chapter discusses the measurement of peak area and deviation of sample composition in the quantitative analysis by gas chromatography GC. Quantitative analysis can in principle be carried out on the basis of either peak height or peak area. The repeatability of peak area is.