PCR testing will also detect genetic material of dead organisms-While there is genetic material present it doesnt mean the organism is the cause of the clinical signs. When using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection the false-negative rates are 38 the day symptoms of COVID-19 appear.
PCRqPCR Qualitative Data Analysis After a traditional PCR has been completed the data are analyzed by resolution through an agarose gel or more recently through a capillary electrophoresis system.
How to interpret real time pcr results. When using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction RT-PCR to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection the false-negative rates are 38 the day symptoms of COVID-19 appear. This rate drops to 20 on the third day after symptom onset and rises steadily to 67 just over two weeks after symptom onset Adapted from Kucirka LM Lauer SA Laeyendecker O et al 2020. Typically all real-time PCR analysis software measures the threshold value as 10 standard deviations from the baseline.
As a result before changing the threshold value the baseline must be established. An amplification curve must have four components. The history the exponential phase the linear phase and the plateau.
Real-time PCR also called quantitative PCR or qPCR can provide a simple and elegant method for determining the amount of a target sequence or gene that is present in a sample. Its very simplicity can sometimes lead to problems by overlooking some of the critical factors that make it work. How to interpret Real time PCR data.
How to calculate relative gene expression in real time PCR if Ct value of reference sample is undetermined or comes almost 37 or so. Interpreting real-time PCR results that are numerical and lend themselves to analytical evaluation. Threshold cycle number How does real-time quantification work.
Most quantitative approaches assume that E is constant during the exponential phase for any given PCR. Several dilutions of an external standard are amplified together with unknown samples. Cycles of PCR Flurescence Real-time PCR has many benefits over the old fashioned approach.
Firstly it gives you a look in to the reaction. You can literally see which reactions have worked well and which have failed. The efficiency of the reaction can be precisely calculated.
There is also no need to run the PCR product out on a gel after. The results of RT PCR tests are obtained based on the end-step of the whole technique process. A fluorescent probe glows if the genetic material of the virus that causes COVID-19 is detected during the PCR technique.
Real-time PCR automates this otherwise laborious process by quantitating reaction products for each sample in every cycle. The result is an amazingly broad 107-fold dynamic range with no user intervention or replicates required. Data analysis including standard curve generation and copy number calculation is performed automatically.
The average turnaround time for PCR nasal swab lab results is currently 3 to 5 days but can take longer depending on lab partner and other factors. All PCR testing is performed by one of our commercial lab partners. The testing platforms used are Roche Cobus or Hologic Panther both with Emergency Use Authorization by the FDA.
RealTime StatMiner Fold change results comparing CNT versus TNT. Upregulated detectors take positive values while repressed detectors are negative. Detectors in blue are expressed in both tissues Detectors in yellow are not expressed in CNT detectors in red are not expressed in TNT and those in black are.
The typical result of a real time PCR analysis with a detection system based on two dyes is an amplification plot with a curve for each detector Figure 4. Since the level of fluorescence signal is variable depending on the dye a threshold value will be independently set for each curve. A standard real time RTPCR set-up usually goes through 35 cycles which means that by the end of the process around 35 billion new copies of the sections of viral DNA are created from each strand of the virus present in the sample.
For the 37 double-negative PCRs samples the Ct values obtained on BD MAXTMwere 2000 for 405 of cases. Positive culture cases had Ct values 30 in 962 and FI 2000 in 988. We showed that the Ct values obtained on BD MAXTMcan help to interpret the results.
The cycle numbers are printed across the bottom. Real-time PCR always goes for 40 cycles. On the y axis is the deltaRn or the change in fluorescence from the previous cycle.
This is the first derivative of the actual fluorescence. While a positive result is easier to interpret it does not necessarily mean a patient has the disease. Remember the following-A viable organism is not needed for testing.
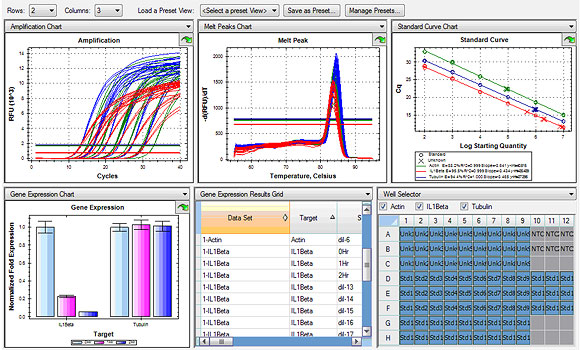
PCR testing will also detect genetic material of dead organisms-While there is genetic material present it doesnt mean the organism is the cause of the clinical signs. Export results for publication Quickly export any charts or tables by right clicking in the window and selecting Save Image As Figure 3 or Export to Excel Figure 4. You can also create reports or real-time PCR data markup language RDML files for quick import into qbase software.
This bands probably are the primer dimers products that can occur during the PCR because the annealing of primers each others. Usually they do not compromise the PCR results and the forward experiments because are lost after purification of PCR product. You could try to use less primers concentration but in my opinion is not a big problem.
PCRqPCR Qualitative Data Analysis After a traditional PCR has been completed the data are analyzed by resolution through an agarose gel or more recently through a capillary electrophoresis system. For some applications a qPCR will be run with the end-point. Real-time PCR is carried out in a thermal cycler with the capacity to illuminate each sample with a beam of light of at least one specified wavelength and detect the fluorescence emitted by the excited fluorophoreThe thermal cycler is also able to rapidly heat and chill samples thereby taking advantage of the physicochemical properties of the nucleic acids and DNA polymerase.