Eonset Emax and the maximum in the tan delta peak. Glass Transition Temperature referred herein as Tg is the point at which a material goes from a hard brittle state to a soft rubbery state.

Amorphous polymers only have a Tg.
How to measure glass transition temperature. Differential Scanning Calorimetry the official method and Thermo-Mechanical Analysis TMA. Glass Transition is a method to characterize a property of a polymeric material. The glass transition is the temperature where the polymer goes from a hard glass like state to a rubber like state.
The best way to envision this type of. 120 Zeilen How to Measure Glass Transition Temperature In DTA the difference in temperature between the sample and a reference material is monitored against time or. In DSC the difference in heat flow to a sample and to a reference is monitored against time or temperature while the.
It is not clearly defined however how the slope changes and the green marked linear sections should be found. It is necessary to rely in a reasonable personal judgement. Determination of the glass transition temperature by DTADSC.
For most Tg values in the literature the DTADSC technique is used. Glass Transition Temperature referred herein as Tg is the point at which a material goes from a hard brittle state to a soft rubbery state. Amorphous polymers only have a Tg.
Crystalline polymers exhibit a Tm melt temperature and typically a Tg since there is usually an amorphous portion as well semi-crystalline. Identifying the Tg of polymers is of interest for various reasons but is most often. The glass transition temperature is a characteristic temperature for the step in the measurement curve.
It can be determined according to various standard methods eg. As the temperature at half the step height or as the point of intersection of the bisector of the angle between the tangents with the measurement. Measurement of the Glass Transition Temperature Using Dynamic Mechanical Analysis O ne of the most fundamental measurements made on polymeric materials is the measurement of the glass transition T g.
In general transitions in materials are associated with different localized or medium-to long-range cooperative motions of molecular segments. Determination of Glass Transition TemperatureThe classical way of measuring glass transition temperature is to perform a series of mechanical tests over the. There are a variety of thermal and mechanical analytical techniques that can be used to measure the glass transition temperature Tg.
Most notably these include. Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC Dynamic Mechanical Analysis DMA and Thermomechanical Analysis TMA depending on the sample. The specific Tg value often depends upon the method and parameters employed so care must be.
10 Zeilen The T g is measured by methods such as Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC. The glass transition temperature of PMCs can be determined by performing a series of tests at increasing temperatures until a sudden drop in the measured property is observed. Note however that a matrix-dominated property of the PMC must be measured in which a significant change occurs when T g is reached.
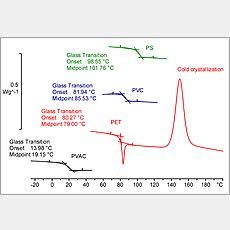
Since performing a series of tests at increasing temperatures is time. The glass transition temperatures T g and the change in the heat capacity were measured using the DSC technique for pure epoxy epoxy with MWCNT addition and epoxy with MWCNT and TP addition. After first scanning to eliminate the thermo stress history the second scanning is recorded for the glass transition temperature measurements.
Over the last decades DSC was routinely used to determine the glass transition temperature of the maximally freeze concentrated solute Tg information which was then applied to freeze-drying process design. Recently Freeze-Dry Microscopy FDM was introduced as a new technology to determine an even more representative critical temperature. The classical way of measuring the glass transition temperature is to perform a series of mechanical tests over the expected temperature range.
While there are several options for the test type flexural strength or shear strength testing are the standards. The glass transition temperature of a polymer can be understood in terms of the Free Volume Theory. The free volume is a measure of the internal space available within a polymer matrix.
When the free volume increases so do the freedom of movement of polymer chains. Glass transitions may occur as the temperature of an amorphous solid is increased. These transitions appear as a step in the baseline of the recorded DSC signal.
This is due to the sample undergoing a change in heat capacity. No formal phase change occurs. As the temperature increases an amorphous solid will become less viscous.
At some point the molecules may obtain enough freedom of motion to. Dynamic moduli as a function of temperature at 1 Hz. As discussed previously when assigning the glass transition temperature Tg both the method of measurement and the convention used to assign the Tg must be noted.
The Tg can be assigned using three different conventions. Eonset Emax and the maximum in the tan delta peak. The glass transition temperature is calculated using a half-height technique which means identifying the midpoint of the kink or the middle of the sloped region.
To understand why a heated amorphous polymer behaves in this fashion its helpful to consider whats happening at the molecular level.