This is a part of the following tutorial. The first step of QC involves checking the volume of reads per sample base qualities and general read.
Hybridization of uorescent mRNA to these probes on the chip is detected by laser scanning of the chip surface.
How to present rna seq data. However a general understanding of the principles underlying each step of RNA-seq data analysis allows investigators without a background in programming and bioinformatics to critically analyze their own datasets as well as published data. Our goals in the present review are to break down the steps of a typical RNA-seq analysis and to highlight the pitfalls and checkpoints along the way that are vital for bench scientists and biomedical researchers performing experiments that use RNA-seq. How to visualize comparative expression data.
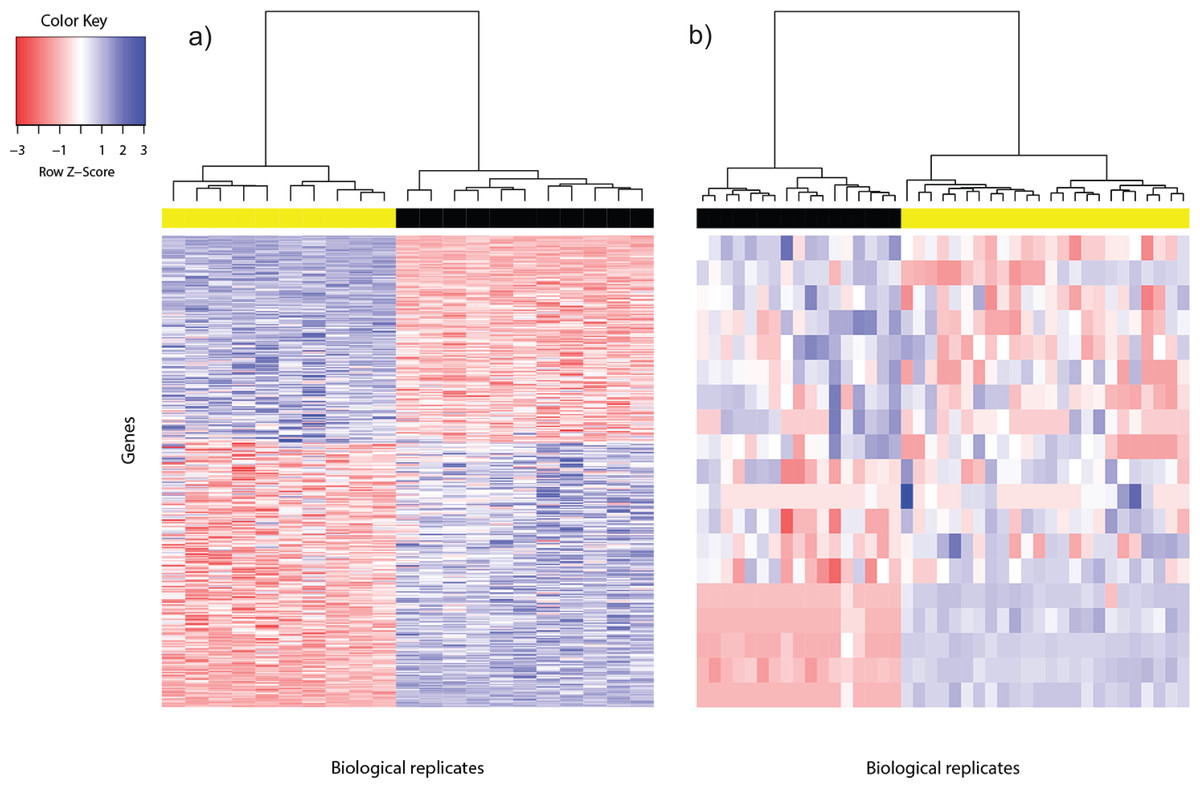
Data is only useful if it is interpretable. When dealing with tens of millions of sequencing reads from an RNA-seq experiment the need for aggregated data that has been cleaned organized and projected clearly is paramount. At the same time dozens of tools exist to help researchers visualize and interpret their RNA-seq data.
Picking the right software and deciding. PolyA-selection Recommended Sequencing Depth. 10-20M paired-end reads or 20-40M reads RNA must be high quality RIN 8 Total RNA.
RRNA depletion Recommended Sequencing Depth. 25-60M paired-end reads or 50-120M reads RNA must be high quality RIN 8. No true consensus exists yet on the most appropriate pipeline for RNA-seq data processing.
However there are numerous online semiautomated tools available such as BaseSpace Illumina MetaCore Thomson Reuters or Bluebee Lexogen. Although these tools generate principal component analysis PCA plots display heat maps and run differential gene expression analysis without the. The deep green reads are uniquely m apped supporting reads nUM4.
The wheat reads are multiply mapped supporting reads. Two supporting reads are redundant so nNR4. There are 4 and 3 uniquely mapped reads grey gr een in upstream and downstream adjacent regions of 40 bp respectively so nUP4 and nDOWN3.
The presence of messenger RNA mRNA is detected by a series of probes that dier in only one nucleotide. Hybridization of uorescent mRNA to these probes on the chip is detected by laser scanning of the chip surface. Aprobe setconsists 11 PM MM pairs the expression level is calculated by synthesizing information from all such PMMM probes.
RNA-sequencing RNA-seq and microarrays are methods for measuring gene expression across the entire transcriptome. Recent advances have made these techniques practical and affordable for essentially any laboratory with experience in molecular biology. A variety of computational methods have been developed.
A basic task in the analysis of count data from RNA-seq is the detection of differentially expressed genes. The count data are presented as a table which reports for each sample the number of sequence fragments that have been assigned to each gene. The acquisition of RNA-seq data consists of several steps obtaining raw reads read alignment and quantification.
At each of these steps specific checks should be applied to monitor the quality of the data Fig. High-throughput RNA sequencing RNA-seq is rapidly emerging as a major quantitative transcriptome profiling platform. Here we present DEGseq an R package to identify differentially expressed genes or isoforms for RNA-seq data from different samples.
In this package we integrated three existing methods and introduced two novel methods based on MA-plot to detect and visualize. WapRNA This is a free web-based application for the processing of high-throughput RNA-Seq data wapRNA from next generation sequencing NGS platforms such as Genome Analyzer of Illumina Inc. Solexa and SOLiD of Applied Biosystems SOLiD.
WapRNA provides an integrated tool for RNA sequence refers to the use of High-throughput sequencing technologies to sequence cDNAs in order to get information about a samples RNA. Use dplyr to explore RNA-seq data Use the split-apply-combine principles to summarise RNA-seq data Make plots with ggplot2 to explore expression changes in an RNA-seq timecourse. This is a part of the following tutorial.
The RNA Seq analysis pipeline demands the presence of multiple checkpoints. The raw reads come in the FASTQ format that stores the ribonucleotide sequences juxtaposed to a per base quality score. The scores can range from 0 to 40.
The first step of QC involves checking the volume of reads per sample base qualities and general read. There are three primary forms of normalization applied to RNA-seq data that help with this and other differences. RPKM or reads per kilobase million was developed in a 2008 paper by Mortazavi et al and is calculated as raw readsexon length x 1000000 mapped reads.
RNA-Seq named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing is a sequencing technique which uses next-generation sequencing NGS to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment analyzing the continuously changing cellular transcriptome.