With the help of these diagrams it can be determined which reactions can take place and which cannot. The scale on the right side of the diagram labelled Po2 is used to determine what partial pressure of oxygen will be in equilibrium with the metal and metal oxide at a given temperature.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
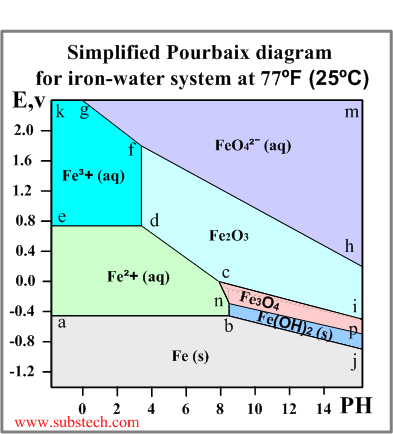
How to read pourbaix diagram. The lines in Pourbaix diagrams represent redox and acid-base reactions and are the parts of the diagram where two species can exist in equilibrium. For example in the Pourbaix diagram for Fe below the horizontal line between the Fe 3 and Fe 2 regions represents the reaction ceFe3_aq e- Fe2_aq which has a standard potential of 077 V. The Pourbaix diagram is a projection of the equilibrium potential surface in a many dimensional parameter space onto the subspace of pH.
When other conditions deviate from the standard conditions the equilibrium potential curve will also move on the Pourbaix diagram. To correctly interprete the Pourbaix diagrams we should first locate the reactions ie. Diagrams represent the stability of a metal as a function of potential and pH.
At a particular combination of pH and potential a stable phase can be determined from the Pourbaix diagram. In such diagrams the redox potential of the corroding system is plotted on a vertical axis and the pH on a horizontal axis. Pourbaixs diagram predicts that Pt metal will dissolve as Pt 2 during anodic polarization in strong acid solutions.
In sulfuric or nitric acid solution the electrolyte enhances the passivation of Pt especially in 055 M solutions and the extent of corrosion seems to be dependent on the formed platinum oxide 91 which is presumably PtO. 90 In more concentrated sulfuric acid solutions of. In summary Marcel Pourbaixs statement means that the Pourbaix diagrams named after him theoretically describe all reactions for the system under consideration that are possible from the point of view of equilibrium thermodynamics.
With the help of these diagrams it can be determined which reactions can take place and which cannot. However irreversible processes such as corrosion reactions cannot be described using Pourbaix diagrams. It is common practice to superimpose these two lines a and b on Pourbaix diagrams to mark the water stability boundaries.
Example problem 48 Some fuel cells operate by oxidizing hydrogen gas on an anode while reducing oxygen from ambient air in contact with a cathode. Pourbaix diagrams have been used extensively to evaluate stability regions of materials subject to varying potential and pH conditions in aqueous environments. However both recent advances in high-throughput material exploration and increasing complexity of materials of interest for electrochemical applications pose challenges for performing Pourbaix analysis on multidimensional systems.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Simplified Pourbaix diagram for 1 M iron solutions. Low E or pE values represent a reducing environment.
High E values represent an oxidizing environment. The pE scale is intended to represent the concentration of the standard reducing agent the e- analogously to the pH scale representing the concentration of standard acid H. PE values are obtained from reduction potentials by dividing E o.
Pourbaix diagrams are plotted by using the Nernst equation an equation used to calculate electrode potential. As the Nernst equation is derived entirely from thermodynamics the Pourbaix diagram can be used to determine which species metals or alloys is thermodynamically stable at a given electrode potential E and pH. The normal Pourbaix-Diagram only shows the corrosivity immunitycorrosionpassivity by 25C.
I am interested in how this varies depending on temperature. Pourbaix diagram handbook 1. The simplest type of these diagrams is based on a chemical system consisting of one element and a water solution for example the Mn-H 2O system.
The system can contain several types of species such as dissolved ions condensed oxides hydroxides oxides etc. The E - pH diagram shows the stability areas of these. Eh and pH axes.
In an Eh-pH diagram the solid stability area is related to the saturation condition and dominant aqueous species give us fundamental information on sorption and colloid phenomena as well as surface characteristics of materials. Eh-pH diagrams are thus essential to understanding solute and radionuclide transport in groundwater. The Pourbaix diagram is an ordinary potential phase diagram for H 2 O and selected contents of the additional components.
The axes are the thermodynamic potentials. The diagram is sectioned at the temperature and pressure of interest usually 25C and 1. A Pourbaix diagram plots the equilibrium potential E e between a metal and its various oxidised species as a function of pH.
The extent of half-cell reactions that describe the dissolution of metal. M M z ze-depend on various factors including the potential E pH and the concentration of the oxidised species M z. The Pourbaix diagram can be thought of as analogous to a phase.
Pourbaix Diagrams plot electrochemical stability for different redox states of an element as a function of pH. As noted above these diagrams are essentially phase diagrams that plot the map the. As noted above these diagrams are essentially phase diagrams that plot the map the.
The scale on the right side of the diagram labelled Po2 is used to determine what partial pressure of oxygen will be in equilibrium with the metal and metal oxide at a given temperature. The significance of this is that if the oxygen partial pre ssure is higher than the equilibrium value.
