Twenty of the 104 cases had a history of papillary neoplasms of the bladder while the remaining 84 cases did not. This type of cancer can generally be broken down into two categories.
In either case the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder.
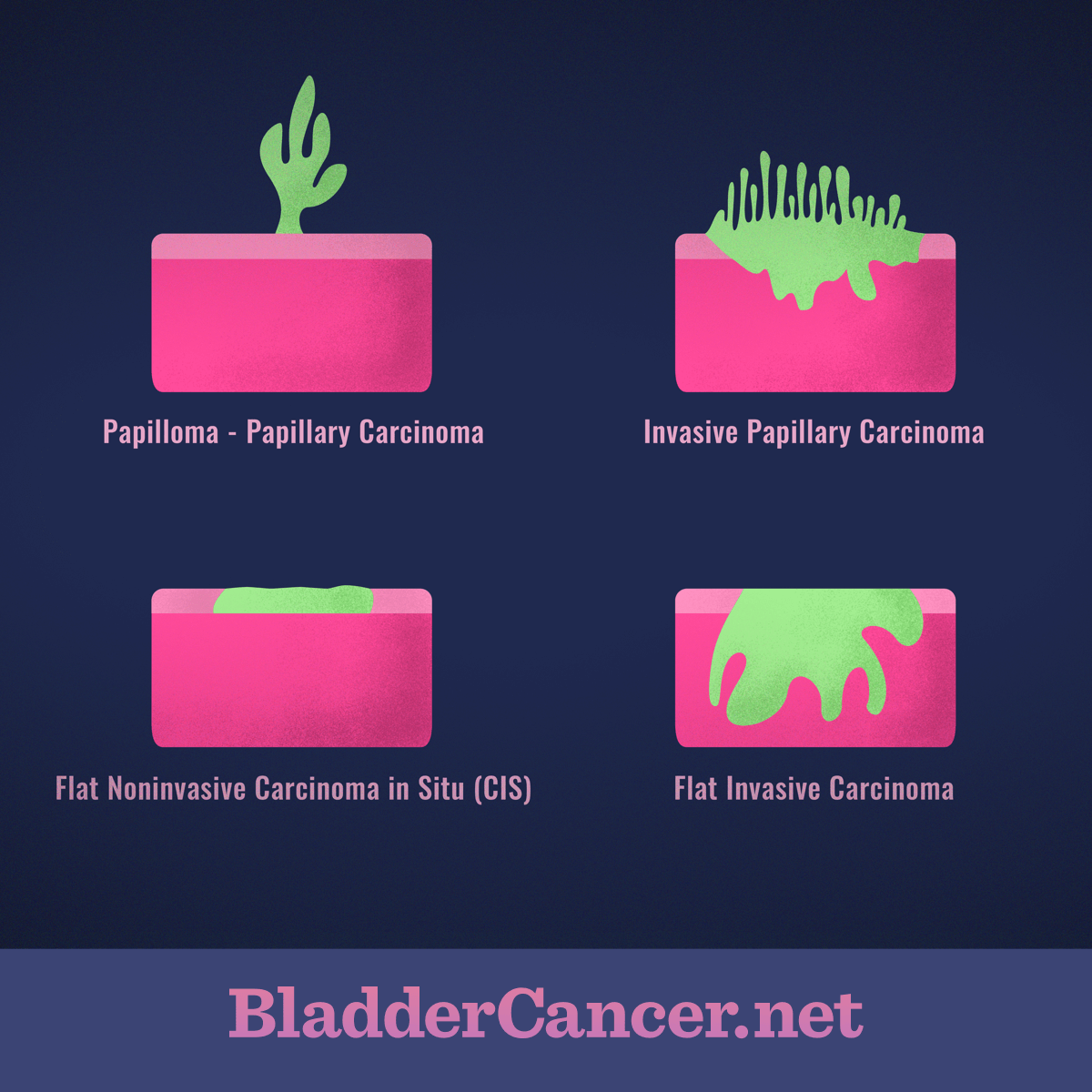
Invasive papillary carcinoma bladder. Urothelial carcinoma also known as transitional cell carcinoma is a type of bladder cancer that starts in the surface of the bladders lining. It can also be referred to as Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer or NMIBC. This type of cancer can generally be broken down into two categories.
One-hundred and four consecutive cases of invasive bladder carcinoma were studied. Twenty of the 104 cases had a history of papillary neoplasms of the bladder while the remaining 84 cases did not. Further 22 of the 104 cases had cystoscopies months to years prior to the diagnosis of invasive bladder carcinoma which documented the absence of previous papillary neoplasms of the bladder.
Therefore this study suggests that papillary neoplasms of the bladder. Invasive urothelial carcinoma may be associated with a papillary carcinoma most commonly high grade or CIS. Most invasive urothelial carcinomas are high grade but grade is not as important for prognosis once the tumor has become invasive.
The extent of invasion is the most significant prognostic factor and determines the type of therapy. Understaging a tumor in a bladder biopsy is a common. The recommendations of this working panel apply to patients with papillary stage Ta and T1 tumours as well as to car-cinoma in situ CIS a flat neoplasm.
The classification of non-muscle-invasive tumours Ta T1 and CIS is given in the TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours 7th Edition 2009 Table 1. Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma Ta and flat non-invasive carcinoma Tis or carcinoma in situ. In either case the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder.
It has not invaded spread deeper into the bladder wall. Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells it is known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or aflat carcinoma in situ CIS.
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder it is called an invasive transitional cell or. The bladder cancer genome atlas project provided analysis of 131 muscle-invasive urothelial carcinomas in an effort to describe molecular alterations and ideally provide insight into use of molecularly targeted agents for both muscle-invasive and NMIBC. The NMIBC community is fortunate to have a multitude of clinical trials currently in this disease space the vast majority of which are.
Noninvasive papillary urothelial neoplasm with moderate to marked cytoarchitectural abnormality. Complex solid to fused papillary architecture nuclear atypia pleomorphism may be focal crowded and overlapping cells brisk mitotic activity. Immunohistochemistry not required for diagnosis.
Commonly presents with hematuria. The primary tumour in the bladder which was treated by partial cystectomy consisted of areas of conventional high grade invasive into the lamina propria papillary urothelial carcinoma with separate myxoid areas. The latter component accounted for 25 of the tumour.
Copyright  1976 by The Williams Wilkins Co. NON-INVASIVE PAPILLARY CARCINOMA OF THE BLADDER ASSOCIATED WITH CARCINOMA IN SITU ALEX F. DALY From the Urological Service and Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston Massachusetts ABSTRACT We evaluated 129 patients with low grade low stage transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder.
We collected bladder transurethral resection specimens showing non-invasive high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma with non-hierarchical secondary papillae lacking fibrovascular cores ie. Cases with any invasive component or any prior history of invasive urothelial carcinoma were excluded. Twenty cases were identified from 16 male and two.
Papillary urothelial carcinoma is a type of cancer. It commonly starts in the bladder but it can also start in the ureters or the urethra. Tumours that show invasion are more aggressive and may require additional treatment.
The anatomy of the bladder and ureters. Definition general Neoplastic proliferation of the urothelium in a papillary configuration with no invasion through the basement membrane Low grade architectural and cytologic abnormality absence of high grade features such as irregular nuclei with frequent prominent nucleoli and.