Electro-luminance is the property of the material to convert electrical energy into light energy and later it radiates this light energy. The LED stands for light-emitting diode and in the below figure you can see the symbol of LED.
First in the LED wafer PN junctions are formed by liquid or vapor epitaxial growth.
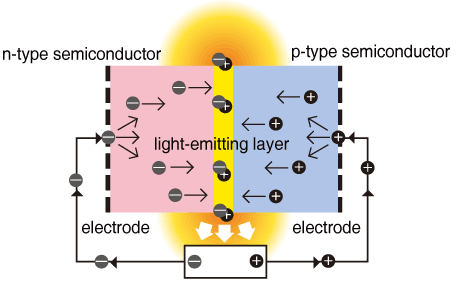
Led structure and operating principle. A light-emitting diode is a two-lead semiconductor light source. It is a pn junction diode that emits light when activated. When a suitable voltage is applied to the leads electrons are able to recombine with electron holes within the device releasing energy in the form of photons.
Physical Structure of LED. LED is structured in such a way so that light emitted does not get reabsorbed into the material. So it is ensured that the electron-hole recombination takes place on the surface.
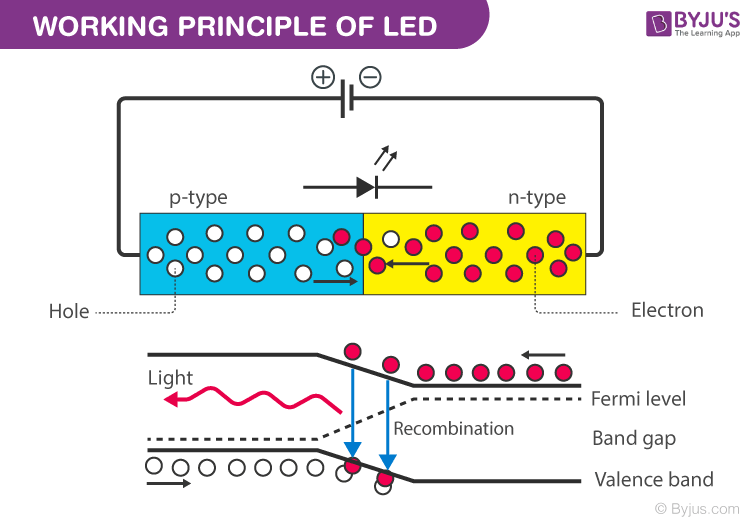
The above figure shows the two different ways of structuring LED p-n junction. The p-type layer is made thin and is grown on the n-type substrate. Working Principle of LED The holes lie in the valence band while the free electrons are in the conduction band.
When there is a forward bias in the p-n junction the electron which is a part of the n-type semiconductor material would overrun the p-n junction and join with the holes in the p-type semiconductor material. So lets get started with Working Principle of LED. Working Principle of LED.
The LED stands for light-emitting diode and in the below figure you can see the symbol of LED. The working of LED is very simple when led is in forward biasing conditions the electrons existing in N side of diode cross the PN junction and enter in the P region combine with the holes existing in that region and emit. A light emitting diode LED is known to be one of the best optoelectronic devices out of the lot.
The device is capable of emitting a fairly narrow bandwidth of visible or invisible light when its internal diode junction attains a forward electric current or voltage. The visible lights that an LED emits are usually orange red yellow or green. LED technology is taken for granted as LEDs are in widespread use.
However the technology and the materials used are key to understanding how a LED works. Although the basic PN junction had been in use for many years it was not until 1962 that the LED was developed and its action started to be understood. Light emitting diode LED circuit symbol.
Working Principle Light Emitting Diode The light LED works on the same principle of simple PN junction diode means when the anode is connected to positive terminal of dc supply and cathode is connected to the negative terminal of dc supply then the PN junction is forward biased. Basics of LED Light Emitting Diode As mentioned in the introduction an LED is a semiconductor light source. It consists of a PN Junction Diode and when voltage is applied to the LED electrons and holes recombine in the PN Junction and release energy in the form of light Photons.
This form of LED structure emits light perpendicular to the plane of the PN junction. Restrict the emission to a small active region within device. YPioneered byPioneered by Burrus and Dawson.
YUsed an etched well in a GaAs substrat inorder to prevent heavy absorption ofto. Light Emitting Diode LED works only in forward bias condition. When Light Emitting Diode LED is forward biased the free electrons from n-side and the holes from p-side are pushed towards the junction.
When free electrons reach the junction or depletion region some of the free electrons recombine with the holes in the positive ions. A light-emitting diode LED is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes releasing energy in the form of photons.
Sequences of offline and online mode. Surrounding light is polarized on the upper plate. Light moves along with liquid crystals and twisted at right angle.
Molecules and lights are parallel to the lower analyzer. Light passes through the plate. An LED is a type of p n junction diode that works on the principle of electro-luminance.
A material called electro-luminance is used to convert electrical energy into light energy which later helps in the propagation of light energy. When light is emitted in the front bias it is called a light-emitting diode. From the above explanation its clear that the intensity of light emitted from a source LED in this case will depend on the energy level of the emitted photons which in turn will depend on the energy released by the electrons jumping in between the atomic orbits of the semiconductor material.
LEDs are the opto semiconductor devices which easily converts electric current into illumination or light. Area of the LED is usually less than 1 and many integrated optical components may be used in designing its radiation pattern. It has the major advantage of low manufacturing cost and renders longer life than the laser diode.
Structure The LED chips are manufactured starting from an LED wafer containing internal PN junctions which is then subjected to processes including diffusion and vapor deposition and is finally diced into chips. First in the LED wafer PN junctions are formed by liquid or vapor epitaxial growth. These PN junctions can be made from.
LED Light Emitting Diode is an optoelectronic device which works on the principle of electro-luminance. Electro-luminance is the property of the material to convert electrical energy into light energy and later it radiates this light energy. In the same way the semiconductor in LED emits light under the.