10 may be solved to provide the concentration of analyte in the solvent at time t c t. 12 This solution is only valid for times greater than Tp.

Coefficients can be calculated as for the physic al extraction since the mass transfer is much slower than the reaction rateThe liquid-liquid extraction is a mass transfer process between two phases.
Liquid liquid extraction column diameter calculation. The difficulty of solving the liquid-liquid extraction problem is reduced when the extract product composition is selected for the design variable instead of the solvent inlet flow as will be demonstrated here. 1 Liquid-Liquid Extraction Liquid-liquid extraction consists of extracting. The estimation of the column diameter generally involves iteration.
Once this is fixed specific throughputs become known and the values of the operating variables namely drop size dispersed-phase holdup mass-transfer coefficients and continuous phase axial-mixing coefficient are calculated from explicit empirical equations which are now available in the literature. Liquid-Liquid Extraction Columns density difference absolute value between the continuous and dispersed phases mass volume-1 viscosity of the continuous phase mass time-1 length-1 density of the continuous phase mass volume-1 density of the dispersed phase mass volume-1 interfacial tension between the continuous and dispersed phases. Minimum pilot column diameter to 50mm and requires special efforts to minimize wall bypassing.
It is obvious that these kind of tests require quite some effort of preparation equipment and solvent logistics. With 50 m3m2h a pilot column of ID100 mm requires to handle close to 400 lh liquids feed solvent for a test run. The column diameter and operating conditions.
Close spacing is used with small-diameter columns and where head room is restricted. As it will be when a column is installed in a building. For columns above 1 m diameter plate spacings of 03 to 06 m will normally be used and 05 m 18 in can be taken as an initial estimate.
This would be. For a simple liquidliquid extraction the distribution ratio D and the partition coefficient KD are identical. A The fraction of solute that remains in the aqueous phase after the extraction is given by equation 776.
Qaq1 Vaq DVorg. Liquid-liquid extraction is an important separation technology for a wide range of applications in the chemical process industries CPI. Unlike distillation which is based on boiling point differences extraction separates components based on their relative solubilities in two immiscible liquids.
Liquid flux m3h-m2 to ensure emulsion bands underneath of each tray and at top of tower is within limits. Droplet diameter to see entrainment and should be assessed in conjunction with hole velocity. Residence time of settling rising of phases.
Liquid-liquid extraction also called solvent extraction was initially utilized in the petroleum industry beginning in the 1930s. It has since been utilized in numerous applications including petroleum hydrometallurgical pharmaceutical and nuclear industries. Coefficients can be calculated as for the physic al extraction since the mass transfer is much slower than the reaction rateThe liquid-liquid extraction is a mass transfer process between two phases.
One liquid phase is the feed consisting of a solute and a carrier. The other phase is the solvent. In most chemical engineering curriculums distillation and liquid-liquid extraction LLE do not receive equal billing.
Yet this powerful separations techno. Liquid-liquid or solvent extraction is a countercurrent separation process for isolating the constituents of a liquid mixture. In its simplest form this involves the extraction of a solute from a binary solution by bringing it into contact with a second immiscible solvent in which the solute is soluble.
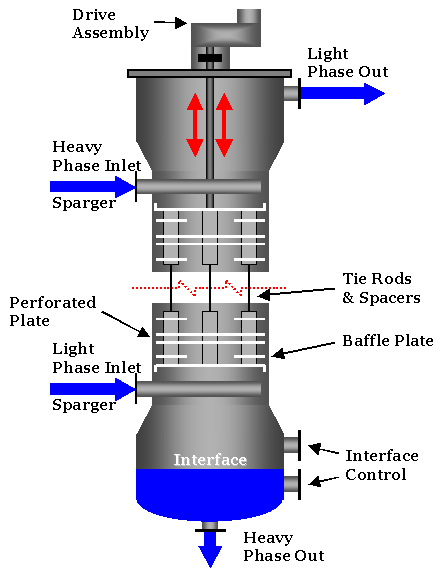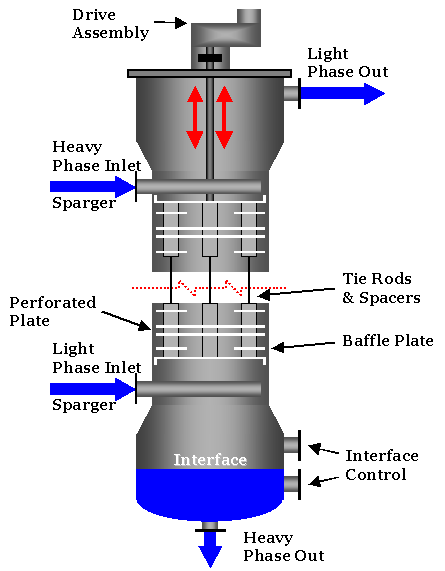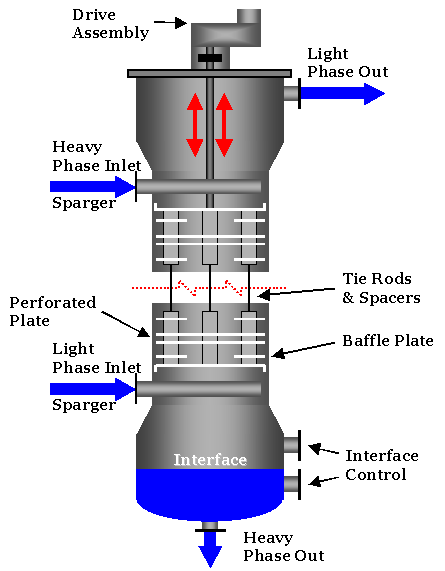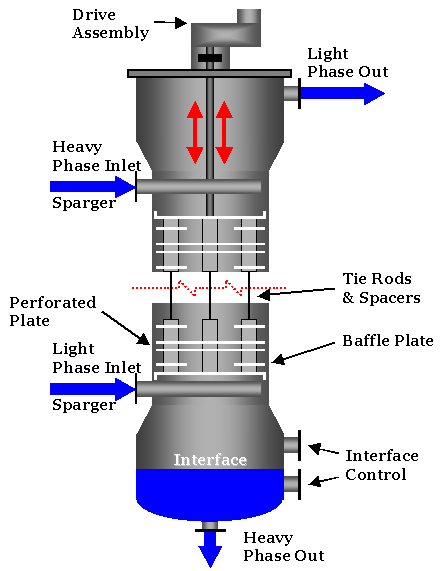
Thus the column diameter can be calculated from the operating parameters V kmolh uvms T K and p bar i. Ds 54 1T3l V 14-28 17p Uy Fig. 143 illustrates liquid-liquid extraction in which the specific gravity of the continuous phase Subscript C is greater than that of the dispersed phase Subscript.
Advantages of Packed Columns 1. For corrosive liquids a packed column will usually be cheaper than the equivalent plate column. The liquid hold-up is lower in a packed column than a plate column.
This can be important when the inventory of toxic or flammable liquids needs to be kept as small as possible for safety reasons. Packed columns are more suitable for handling foaming. And are used with our packed extraction columns.
Advantages and Characteristics Based on the special design of the pack-ing and liquid distributors the ECP col-umn has a number of advantages. High specific throughput resulting in-Small column diameters-Revamp options of existing columns to increase capacity. The basic theory of solvent extraction as well as the operational mechanism of various extractors mixer-settler column extractors and liquid membranes have been described.
If the flow is constant this is given by Tp If- 11 Eq. 10 may be solved to provide the concentration of analyte in the solvent at time t c t. C f Ci exp -z f f Dß t-r.
12 This solution is only valid for times greater than Tp. For times less than Tp it is assumed that c t c. Diameter dn is given as ö or dm fzz2.
2000 Modeling of Liquid-Liquid Extraction Column. A Review empirical correlations for predicting the hold-up in different types of.
