The Metabolome-Wide Association Study. This study aimed to elucidate gut microbiomes role in RA pathology by a comprehensive metagenome-wide association study MWAS.
We were unable to create site-directed mutants for each of the predicted genes in Acetobacter so we created an arrayed transposon insertion library using Acetobacter fabarum.
Metagenome wide association study. To carry out analysis on gut microbial content in patients with type 2 diabetes we developed a protocol for a metagenome-wide association study MGWAS and undertook a two-stage MGWAS based on deep shotgun sequencing of the gut microbial DNA from 345 Chinese individuals. We identified and validated approximately 60000 type-2-diabetes-associated markers and established the concept of a metagenomic linkage group enabling taxonomic species-level analyses. This study aimed to elucidate gut microbiomes role in RA pathology by a comprehensive metagenome-wide association study MWAS.
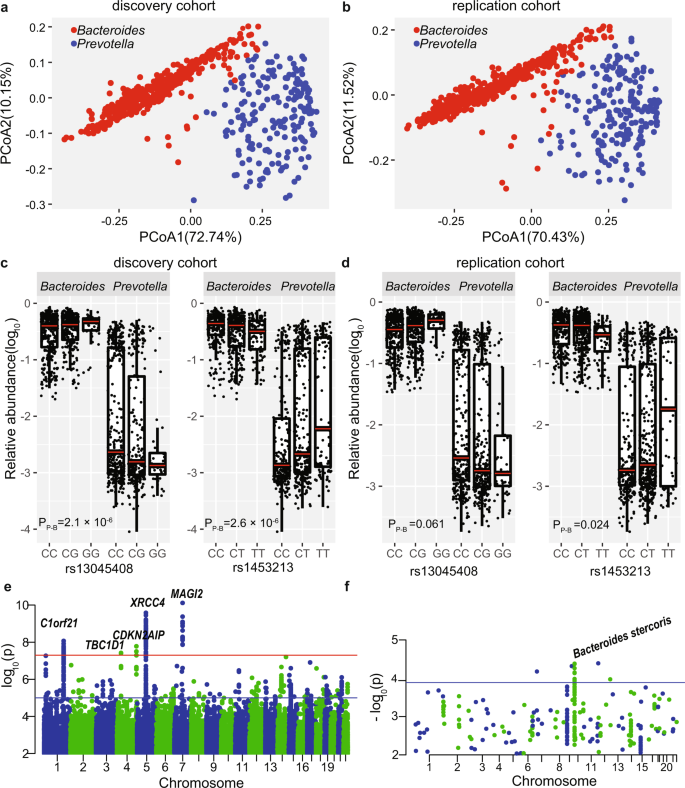
We conducted MWAS of the RA gut microbiome in the Japanese population n case 82 n control 42 by using whole-genome shotgun sequencing of high depth average 13 Gb per sample. Our MWAS consisted of three major bioinformatic analytic. This study aimed to elucidate gut microbiomes role in RA pathology by a comprehensive metagenome-wide association study MWAS.
Methods We conducted MWAS of the RA gut microbiome in the Japanese population n case82 n control42 by using whole-genome shotgun sequencing of high depth average 13 Gb per sample. Our MWAS consisted of three major. A metagenome wide association MGWA study of bacterial host association determinants in Drosophila predicted that LPS biosynthesis genes are significantly associated with host colonization.
We were unable to create site-directed mutants for each of the predicted genes in Acetobacter so we created an arrayed transposon insertion library using Acetobacter fabarum. In this study we employed a metagenome-wide association approach 32 to identify microbial species and functions that could contribute to robust recovery of the microbiome. Metagenome-wide association study MWAS and the RA genome-wide association study GWAS.
Our study indicated a value of metagenome- wide shotgun sequencing rather than classical amplicon sequencing of 16S ribosomal RNA rRNA genes of microbiomes. How might this impact on clinical practice or future developments. To identify new genetic risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis we conducted a genome-wide association study meta-analysis of 5539 autoantibody-positive individuals with rheumatoid arthritis cases and 20169 controls of European descent followed by replication in an independent set of 6768 rheumatoid arthritis cases and 8806 controls.
Of 34 SNPs selected for replication 7 new rheumatoid. We conducted a three-stage genetic study to identify susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes T2D in east Asian populations. We followed our stage 1 meta-analysis of eight T2D genome-wide association studies 6952 cases with T2D and 11865 controls with a stage 2 in silico replication analysis 5843 cases and 4574 controls and a stage 3 de novo replication analysis 12284 cases and.
On the other hand in a metagenome-wide association study with the case-control design one typically sequences the microbial community of a number of patients and normal individuals obtains gene scaffold by assembling the sequencing data mapping sequence reads to the scaffolds to obtain abundance levels of the genes and applies statistical approaches to test whether the abundance level. Large-scale genome-wide association GWA analyses of adult height in Europeans have identified nearly 180 genetic loci. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of adult height in East Asians identifies 17 novel loci Hum Mol Genet.
Epub 2014 Nov 26. Authors Meian He 1 Min Xu 2 Ben Zhang 3 Jun Liang 4. We conducted a meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of systolic SBP and diastolic DBP blood pressure in 19608 subjects of east Asian ancestry from the AGEN-BP consortium followed up with de novo genotyping n 10518 and further replication n 20247 in east Asian samples.
Data from multiple genome-wide association studies are often analyzed together for the purposes of combining information from several studies of the same disease or comparing results across different disorders. We provide a valid and efficient approach to such meta-analysis allowing for overlapping study subjects. The available data may contain individual participant records or only meta.
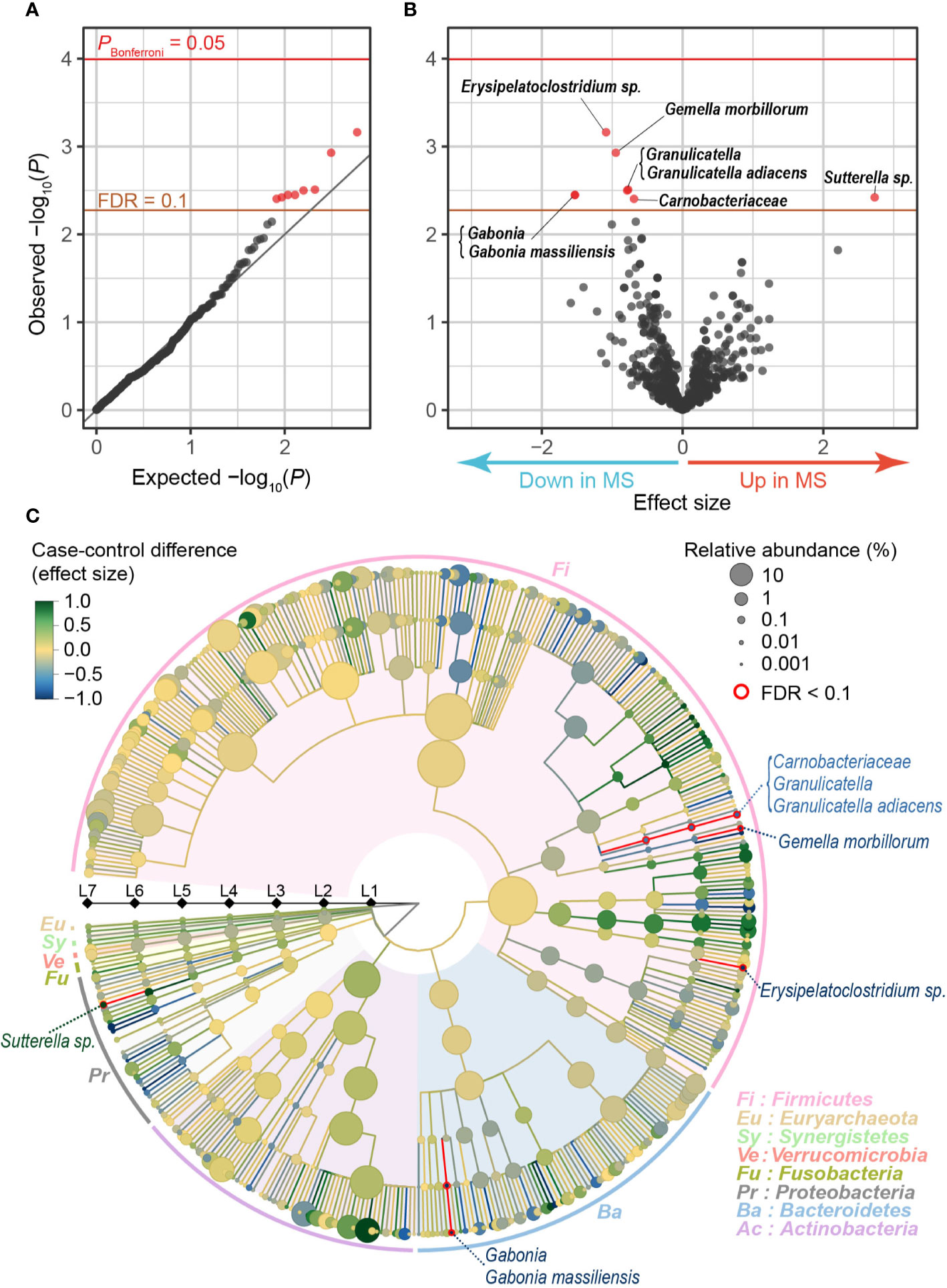
Metagenome-genome-wide association studies reveal human genetic impact on the oral microbiome Xiaomin Liu Xin Tong Jie Zhu Liu Tian Zhuye Jie Yuanqiang Zou Xiaoqian Lin Hewei Liang Wenxi Li Yanmei Ju Youwen Qin Leying Zou Haorong Lu Xun Xu Huanming Yang Jian Wang Yang Zong Weibin Liu Yong Hou Shida Zhu Xin Jin. Here we conducted a comprehensive metagenome-wide association study MWAS of the relapsing-remitting MS gut microbiome ncase 26 ncontrol 77 in the Japanese population by using whole-genome shotgun sequencing. A Metagenome-wide Association Study of Gut Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma Patients The safety and scientific validity of this study is the responsibility of the study sponsor and investigators.
Listing a study does not mean it has been evaluated by the US. Metagenome-wide association studies MWAS are designed to detect associations between the human microbiome and disease. In this Review Jia and Wang describe the principal findings of MWAS of.
The Metabolome-Wide Association Study. A New Look at Human Disease Risk Factors T he ongoing revolution in high-throughput genomic screen-ing and the promise of a deeper understanding of genetic variation in relation to common disease have led to the development of the genome-wide association GWA study paradigm. The concept is straightforward.
We have termed this the metabolome-wide association MWA study concept. We recently demonstrated the first proof of principle of this approach in humans for the identification of discriminatory biomarkers at the population level and their associations with disease risk such as for high blood pressure BP Nature 2008 453 396400. One approach to identify the association is using metagenome-wide association study MWAS which takes advantages of huge taxa data discovered using metagenomics and applies the concept of genome-wide association study GWAS for the association analysis.
