A major step forward in the development of murine models of intestinal inflammation came with. The adoptive T cell transfer model induces chronic small bowel and colonic.
By contrast to generate DSS.
Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. Animal models of intestinal inflammation are indispensable for our understanding of the pathogenesis of Crohn disease and Ulcerative colitis the idiopathic forms of inflammatory bowel disease in humans. The clinical appearance of human IBD is heterogeneous a fact that is also reflected by the stea.
Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease 1. Crohns disease CD and ulcerative colitis UC are chronic inflammatory disorders of the intestine. Animal models of IBD.
Much of the recent progress in the understanding of mucosal immunity has been achieved by the. Currently several mouse models are considered representative of inflammatory bowel disease IBD. This review presents recent developments regarding the role of animal models of intestinal inflammation as research tools in IBD.
UC is restricted to the colon and is manifest as continuous inflammation starting from the rectum and extending back towards the cecum. Inflammation in UC is primarily restricted to mucosal layers. Research is ongoing to understand the causality of these two diseases and advances in understanding of their pathology have resulted from the variety of mouse models of IBD that have.
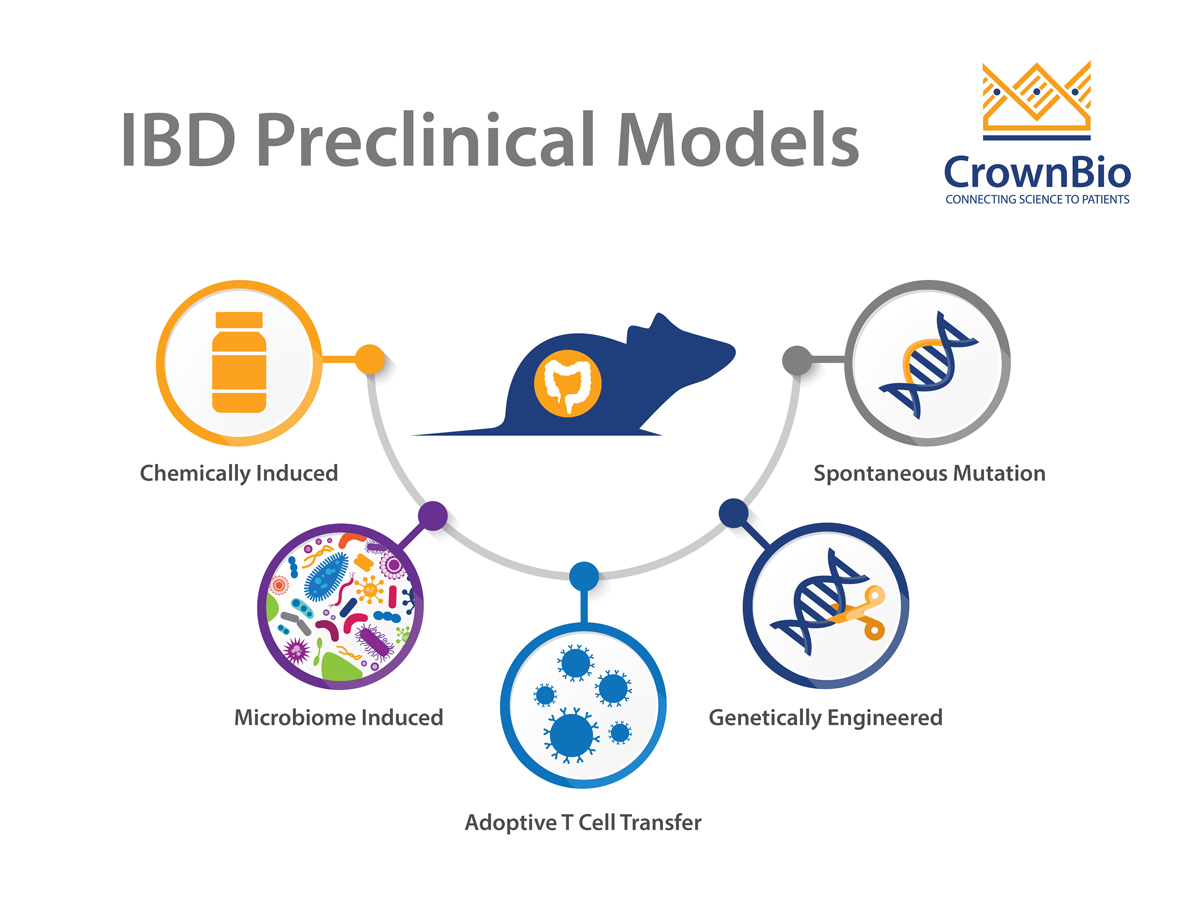
A major step forward in the development of murine models of intestinal inflammation came with the discovery that adoptive transfer of naïve CD4 T cells CD4 CD45RB high T cells from donor mice into syngeneic immunodeficient lymphopenic SCID or Rag1 recipient mice causes a wasting disease and a primarily colonic inflammation that develops 5 to 10 weeks after treatment. Mouse Models For Inflammatory Bowel Disease Studies Chemically Induced Mouse Models. Chemically induced mouse models are the most widely used inflammatory bowel disease.
Adoptive T Cell Transfer Mouse Model. The adoptive T cell transfer model induces chronic small bowel and colonic. The adoptive T cell transfer IBD mouse model recapitulates the clinical pathology colitis and small bowel inflammation observed in human intestinal inflammatory diseases such as a Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis.
Support for Your IBD Program. Which IBD model is best for your program. Chemical and Genetic Mouse Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis An established model of IBD employs the chemical Dextran Sodium Sulfate DSS.
What is already known on this topic Scientists have developed several mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease but Crohns disease has been particularly difficult to model. What this research adds Researchers created a mouse model that recapitulates many hallmarks of gut inflammation seen in people with Crohns disease. Mouse models of intestinal inflammation resemble aspects of inflammatory bowel disease in humans.
These models have provided important insights into mechanisms that control intestinal homeostasis and regulation of intestinal inflammation. This viewpoint discusses themes that have emerged from mouse models of intestinal inflammation including. A major step forward in the development of murine models of intestinal inflammation came with.
Comparison of experimental mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease SOO YOUN OH 1 KYUNG-AH CHO 2 JIHEE LEE KANG 34 KWANG HO KIM 1 and SO-YOUN WOO 2. The gut microbiota in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease. In this review we describe some of the most commonly used mouse models of colitis and Crohns disease.
In TNBS and oxazolone colitis models topical administration of hapten reagents results in T-cell-mediated immunity against haptenized proteins and luminal antigens. By contrast to generate DSS. In this study in order to compare the mechanisms of inflammatory response in mice 3 distinct models of IBD were established.
2 TNBS-induced acute colitis 4 DSS-induced acute colitis and 2 DSS-induced chronic colitis. In addition to evaluate the effects of TNBS on inflammasome activation we used caspase-1 knockout KO mice. Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is a chronic intestinal inflammatory condition that is mediated by very complex mechanisms controlled by genetic immune and environmental factors.
More than 74 kinds of genetically engineered mouse strains have been established since 1993 for. Murine Models of Inflammatory Bowel Disease IBD. Challenges of Modeling Human Disease JASON DEVOSS 1 AND LAURI DIEHL 2 1Department of Immunology Genentech Inc San Francisco California USA 2Department of Pathology Genentech Inc San Francisco California USA ABSTRACT Animal models of human disease are a critical tool in both basic research and drug development.
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD is a chronic multifactorial inflammatory disorder characterized by periods of activation and remission of intestinal inflammation with potentially severe complications that can lead to mortality. Experimental animal models of intestinal inflammation are crucial for understanding the pathogenesis of Crohns disease.
