Some of the more common symptoms are erratic retention times noisy baselines or spikes in the chromatogram. Pumping system problems are usually easy to spot and correct.

Some of the more common symptoms are erratic retention times noisy baselines or spikes in the chromatogram.
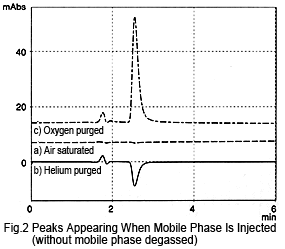
Negative peaks in hplc chromatogram. A negative peak means that there is less absorbance while the peak is passing through the detector than when the mobile phase is passing through. Two likely reasons for this are. 1 The mobile phase has more absorbance than the analyte at the.
Negative peaks are proportional to Positive peaks. It means that the negative and the positive peak height varies with concentration change but the height proportion stays the same. There may be various reasons for negative peaks in HPLC diagrams like impurities or air bubbles in the eluent.
Negative Peaks sind vor allem dann störend wenn sie zum Beispiel vor oder direkt nach einem interessierenden Peak eluieren und dadurch eine problemlose Integration verhindern. In solchen Fällen handelt es sich meistens um Komponenten die tatsächlich dort eluieren. Man sollte nun diese Peaks als ganz normale Peaks behandeln.
Es kann versucht werden durch Verringerung des. If youd see a positive peak immediately followed by a negative peak with the same shape this could indicate an issue with the purge valve. However as the peak shape doesnt match and only one peak is affected I would exclude a hardware issue.
I would suggest to go for known good conditions. This would help to find out wheter your application is to blame or not. In any case frequent flushing and switching.
A negative peak means that there is less absorbance while the peak is passing through the detector than when the mobile phase is passing through. Two likely reasons for this are. 1 The mobile phase has more absorbance than the analyte at the.
A wide range of conditions. Modern HPLC pumps incorpor-ate single or dual piston syringe or diaphragm pump designs. Pumping system problems are usually easy to spot and correct.
Some of the more common symptoms are erratic retention times noisy baselines or spikes in the chromatogram. Leaks at pump fittings or seals will result in poor chromatography. A sure sign of a.
What Are Common Peak Shape Issues. Broad peaks Many peak shape issues are also combinations - ie. Broad and tailing or tailing with increased retention Symptoms do not necessarily affect all peaks in the chromatogram Each.
What causes a negative baseline drift in HPLC. I use a superdex 10300 column and my mobile phase is a filter sterilized wash buffer. Recently I noticed a negative baseline drift in my chromatogram.
Tailing an Basis unscharfe Peaks oft mit verschobener Retentionszeit. Überladung der HPLC Säule. Aufgabekonzentration verringern oder Säule mit höherer Kapazität verwenden.
Fronting ohne Verschiebung der Retentionszeit. Totvolumen zwischen Injektor und Säule. Injektor Tubing auf Totvolumen prüfen.
Information relating to the reasons why negative peaks might be visible in a LCMS chromatogram. What do negative peaks in the Mass Spec chromatogram indicate. Agilent Skip to main content Skip to main content.
Ungewollte Peaks im Chromatogramm sind störend bei der Auswertung und können falsche Ergebnisse liefern wenn sie mit Zielanalyten coeluieren. Daher wird immer versucht statistisch auftauchende Peaks sowie regelmäßige Peaks von Verunreinigungen zu vermeiden. Diese Geisterpeaks können verschiedene Ursachen haben.
Sie können aus den Eluenten kommen aus der Probe oder. Zeigen die Peaks eines Chromatogramms eine eher flache und asymmetrisch nach vorn verlagerte Form so dass es fast aussieht wie ein Doppelpeak Splitpeak ist oft ein zu starkes Probenlösungsmittel die Ursache. Die Injektion der Probe in zu starkem Lösungsmittel führt dazu dass die Bestandteile der Probe mit dem Lösungsmittel mitgeschwemmt werden anstatt sich vernünftig an die Säule binden zu können.
Wenn möglich sollten daher die HPLC. HPLC pumps incorporate single or dual piston syringe or diaphragm pump designs. Pumping system problems are usually easy to spot and correct.
Some of the more common symptoms are erratic retention times noisy baselines or spikes in the chromatogram. Leaks at pump fittings or seals will result in. A Recorder lead reversed.
B Refractive Index of solute less than of mobile phase RI detector. Use mobile phase with lower refractive index or reverse recorder leads. C Sample solvent and mobile phase differ greatly in composition UVdetector.
Adjust or change sample solvent. Negative peaks appear when the sample solvent and mobile phase differ greatly in composition or the mobile phase might be more absorptive than sample components to the set UV wavelength. Discover our HPLC products.
Negative peaks are most often caused by difference in refractive index between the sample solvent sample and mobile phase. They are also caused after routine maintenance when the system has not been reconfigured correctly. Armelle Vallat Mai 2007 24.
ApexTrack Integration Timed Events Allow Negative Peaks Event. ApexTrack detects negative peaks as apices that have curvatures whose sign is opposite that of positive peaks. Negative peaks can be isolated or part of a cluster.
In a cluster adjoining peaks can have the same or opposite signs for height. You must activate negative peak detection by entering an Allow Negative. A short video which shows how to use the FLIP and CLAMP integration timed events within the Chromperfect chromatography data system.