
Argument of periapsisω vi. An orbit in which the satellite moves in a direction counter to the earths rotation.
Near space is quantitatively defined as the range of earth altitudes from 20 km to 100 km below which heavier-than-air aircraft can produce sufficient lift for steady flight above which the atmosphere is rarefied enough for satellites to orbit with meaningful lifetimes Young et al 2009 and the altitude between 20 km and 50 km is suitable for buoyant lighter-than-air systems.
Orbital parameters of a satellite. An orbit in which the satellite moves in a direction counter to the earths rotation. The inclination of a retrograde orbit always lies between 90 and 180. The inclination of a retrograde orbit always lies between 90 and 180.
WHAT ARE THE ORBITAL PARAMETERS. Orbital elements of a satellite are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In astronomy and orbital mechanics there are overall six parameters used to define an orbit.
Inclination or tilti iv. Longitude of the ascending nodeΩ v. Argument of periapsisω vi.
Mean anomaly at epochv. Planetary Satellite Mean Orbital Parameters. Select from satellites of Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto.
These mean orbital parameters are not intended for ephemeris computation. Accurate ephemerides should be obtained from our HORIZONS system. Mean orbital parameters are primarily useful in describing the general.
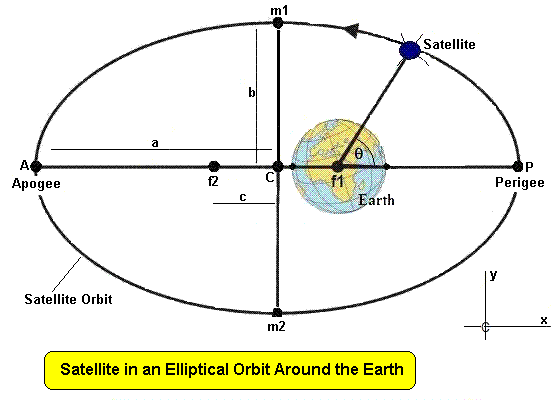
The satellite height is characterized by the orbits semimajor axis a the variation in the radial distance due to the ellipticity of the orbit the eccentricity e and the angular distance v the true anomaly from the point of closest approach in the orbit called the Perigee. Orbital elements are the parameters which are helpful for describing the orbital motion of satellites. Following are the orbital elements.
Right ascension of ascending node. The above six orbital elements define the orbit of earth satellites. Therefore it is easy to discriminate one satellite from other satellites based on.
Satellite in its orbit relative to perigee. At perigee the Mean Anomaly is zero it increases to 180 degrees at apogee then back to perigee at 360 degrees. Since the orbit is often not a circle the measurement of the angle is difficult so the angle is expressed in terms of a.
Only one parameteris needed to specify the size of the orbit and that is the radius rthe constant distance from the centre of the Earth to the satellite. If the radius of the Earth is denoted by Re then the altitude orheight of the orbit and the satellite above the Earths surface ish r - Re. Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraftThe motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newtons laws of motion and law of universal gravitationOrbital mechanics is a core discipline within space-mission design and control.
Orbit of a SatelliteAn artificial satellite moves around the earth or any other celestial body in a path which is called its orbitWe put a man made satellit. 1Concept of Apogee 2Concept of Perigee 3Line of Apsides 4Line of nodes 5Ascending nodes 6Descending nodes 7Orbital parameter in satel. Near space is quantitatively defined as the range of earth altitudes from 20 km to 100 km below which heavier-than-air aircraft can produce sufficient lift for steady flight above which the atmosphere is rarefied enough for satellites to orbit with meaningful lifetimes Young et al 2009 and the altitude between 20 km and 50 km is suitable for buoyant lighter-than-air systems.
The satellites orbit in a circular low Earth orbit at about 500 km 310 mi altitude in a high-inclination orbit for a planned six to twelve-month duration. Used orbital parameters of a GPS satellite in space engine to see what the earth looks like from there. 2 20210429 0309 Male 60 years old level or over An engineer Useful Purpose of use.
Orbit determination of an artificial satellite requires as input measurements that are related to the satellites position or velocity. These data are collected by a satellite tracking system that. Seven numbers are required to define a satellite orbit.
This set of seven numbers is called the satellite orbital elements or sometimes Keplerian elements after Johann Kepler 1571-1630 or just elements. These numbers define an ellipse orient it about the earth and place the satellite on the ellipse at a particular time.