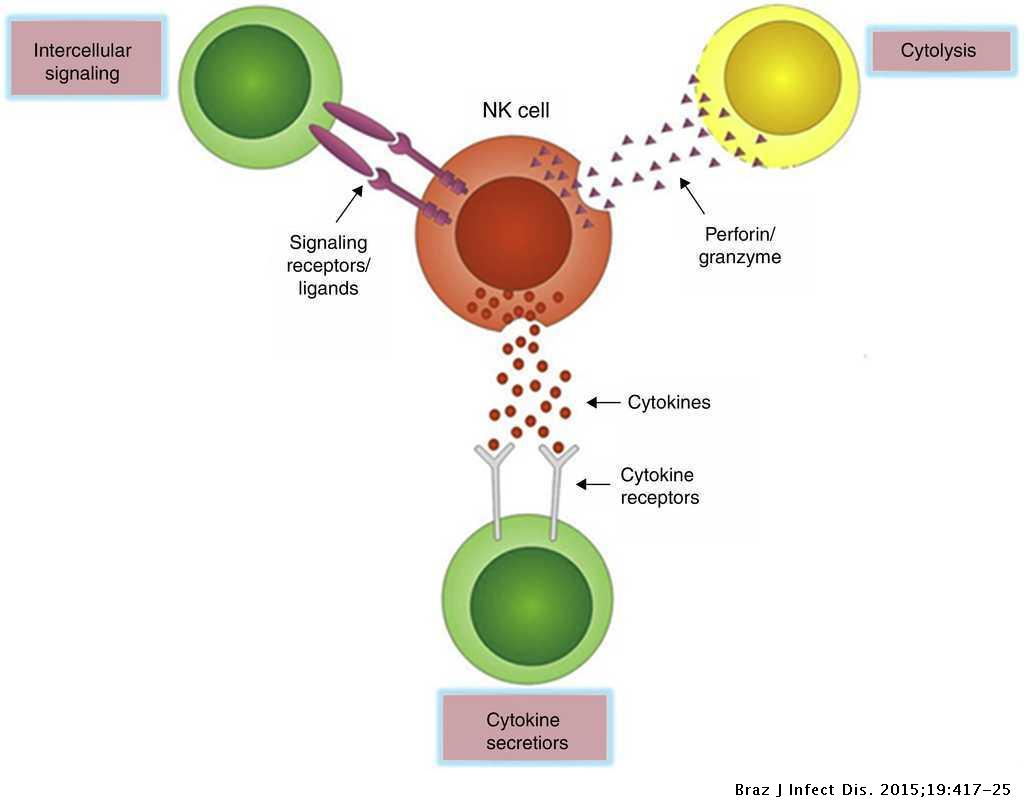
In addition to being a potent innate source of IFN-γ NK cells hold cytoplasmic granula that contain perforin and granzymes involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Perforin is a pore forming cytolytic protein found in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes CTLs and natural killer cells NK cells.
In addition to being a potent innate source of IFN-γ NK cells hold cytoplasmic granula that contain perforin and granzymes involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
Perforins are cytolytic chemicals used by nk cells. Perforins are cytolytic chemicals used by NK cells. Asked by Wiki User. Wiki User Answered 2012-03-03 021103.
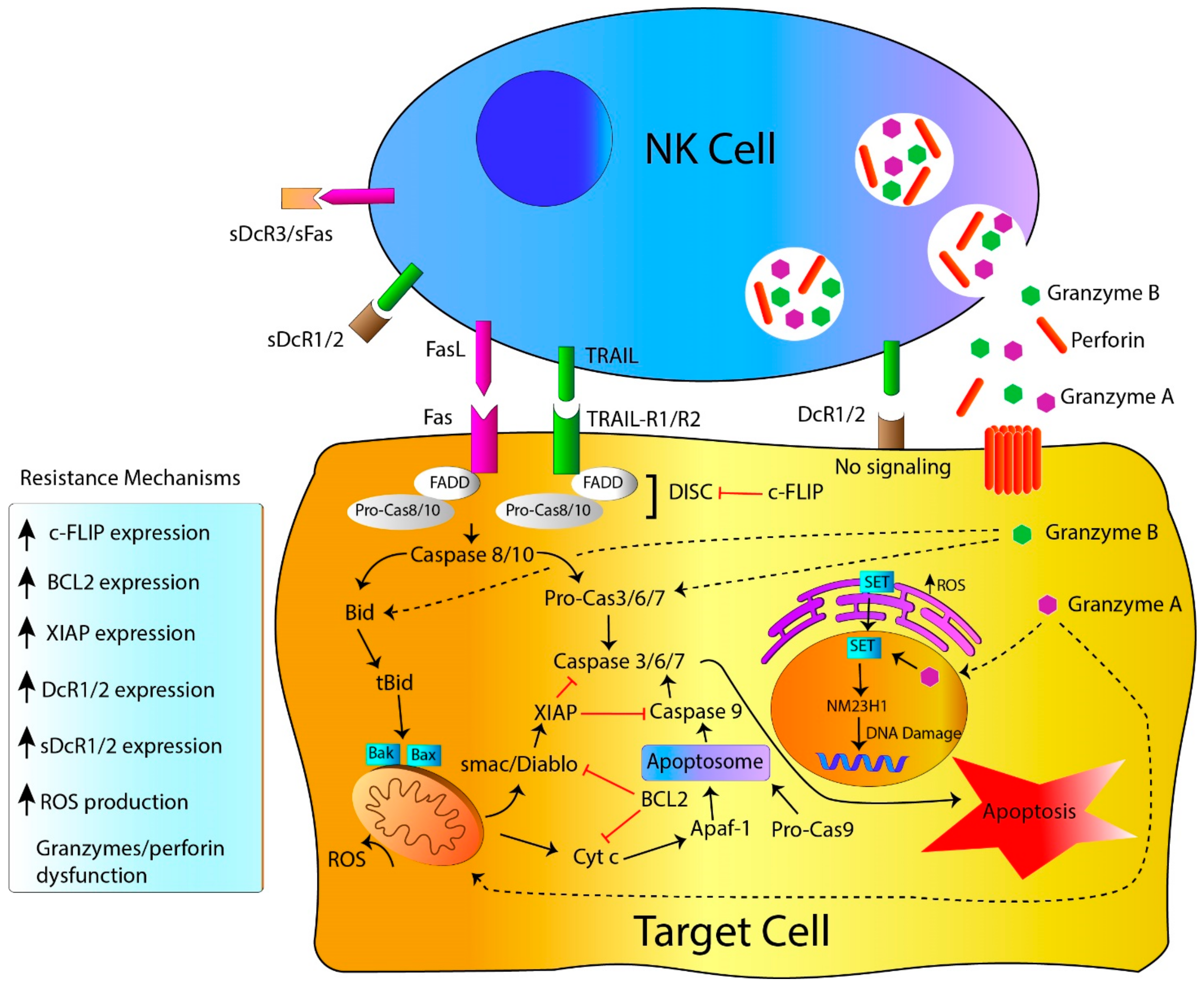
Perforin is a pore forming cytolytic protein found in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes CTLs and natural killer cells NK cells. Upon degranulation perforin binds to the target cells plasma membrane and oligomerises in a Ca2 dependent manner to form pores on the target cell. Cytotoxic T- and NK cells express cytoplasm granules containing cytolytic effector molecules as perforins studied here which can recognize and destroy damaged infected andor mutated target cells.
Protozoan infections are a serious global health problem. Natural killer NK cells and cytolytic T lymphocytes CTLs eliminate pathogen-infected cells by releasing cytolytic granule contents–granzyme Gzm proteases and the pore-forming perforin PFN–into the infected cell. However these cytotoxic molecules do not kill intracellular parasites.
The underlying mechanism is contact dependent and requires two cytolytic proteins. Mycobacteria induce enhanced expression of the cytolytic proteins via activation of the NKG2DNCR cell-surface receptors and intracellular signaling pathways involving ERK. Perforins are cytolytic chemicals used by NK cells.
Somatic recombination by B cells allows each B cell to form its own unique antibody genes. Which of the following is characteristic of antibodies. Perforins are toxic chemicals that punch holes into the cell membrane of an infected cell to lyse the cell.
Perforins are cytolytic chemicals used by NK cells. Like cytolytic T cells CTLs NK cells have cytoplasmic granules containing perforins and granzymes which kill target cells. But there are differences between NK cells and CTLs with respect to their target cell killing.
The NK cell activity does not require any previous exposure to the antigens. To investigate whether an altered distribution of perforins in cytolytic cells or a reduced number of cytolytic cells producing perforins underlies decreased cytolytic activity with advancing age perforin expression was assessed at the single cell level in T- CD4 and CD8 and NK CD16 peripheral blood lymphocytes from elderly subjects by flow cytometry. Which of the following is true of immediate hypersensitives.
A also called type IV hypersensitivities. B are adaptive immune responses to disease organisms. C include allergic contact dermatitis.
D involve IgE antibodies and the release of histamine from mast cells and basophils. Perforin encoded by the gene PRF1 is located within cytolytic granules inside cytotoxic T cells and natural killer NK cells. When the cytotoxic cell recognizes a transformed or infected target cell the granules containing Perforin granzymes and granulysin migrate to the cell membrane and release their contents into the immune synapse 40.
Glycoproteins with cytolytic properties are located in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and NK cells. After release to the surface of target cells perforins undergo polymerisation to form polyperforins which perforate the phospholipid double layer of the cytoplasmic membrane. The damaged membrane causes cell death and lysis.
Cancer cells and virus-infected body cells can be killed before activation of adaptive immunity by natural killer cells Complement proteins and antibodies coat a microorganism and provide binding sites enabling macrophages and neutrophils to phagocytize the organism. A cytolytic protein secreted by NK cells is _____ a perforin b granzyme a. Granzymes are secreted by NK cells but they are protein degrading enzymes.
35 _____ lymphocytes originate in the red bone marrow then finish maturation in the thymus. A T b B a. B cells originate in the red bone marrow but do not reside in the thymus 36.
The NK cell is then able to contact the cell and release pore-forming proteins called perforins and proteolytic enzymes called granzymes. Granzymes pass through the pores and activate the enzymes that lead to apoptosis of the infected cell by means of destruction of its structural cytoskeleton proteins and by chromosomal degradation. In addition to being a potent innate source of IFN-γ NK cells hold cytoplasmic granula that contain perforin and granzymes involved in cell-mediated cytotoxicity.
NK cells express various types of immunoreceptors that are all designed to sense pathological changes of self cells. In NK cells and T cells granzymes are packaged in cytotoxic granules along with perforin. Granzymes can also be detected in the rough endoplasmic reticulum golgi complex and the trans-golgi reticulum.
The contents of the cytotoxic granules function to permit entry of the granzymes. Perforin is a pore forming cytolytic protein found in the granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes CTLs and natural killer cells NK cells. Upon degranulation perforin binds to the target cells plasma membrane and oligomerises in a Ca2 dependent manner to form pores on the target cell.