
The difference is the slip. The synchronous speed is 1500 rpm and the typical full load speed is 1450 rpm.
Induction motor full load torque depend upon supply voltage slip and rotor resistance.
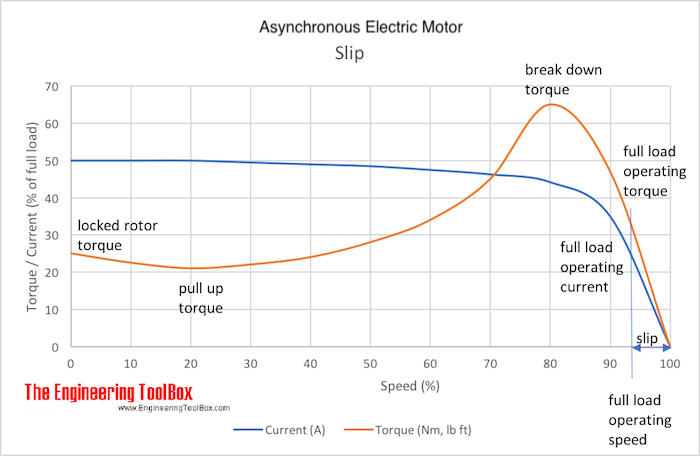
Slip of induction motor at full load. The value of slip in induction motor at full load varies from about 6 for small motors to about 2 for large motors. Significance of Slip in Induction Motor Slip of induction motor plays an important role in the operation of the induction motor. The torque produced by the induction motor is directly proportional to induction motor slip.
This is never possible in induction motor at any condition. Practically slip maintains 001 to 005. It means 1 to 5.
The Slip which is corresponding to the full load speed of the motor is called as Full load Slip. Why induction motor Takes high starting current. When the rotor is not turning the slip is 100.
Full-load slip varies from less than 1 in high hp motors to more than 5-6 in minor hp motors. Number of poles frequencies and synchronous induction motor speed. So slip of induction motor can not be zero under any circumstances.
Practically motor operates in the slip range of 001 to 005 ie. 1 to 5. The slip corresponding to full load speed of.
As one can see full-load slip varies from less than 1 percent in high-hp motors to more than 5 percent in fractional-hp motors. These variations may cause load-sharing problems when motors of different sizes are connected mechanically. At low load the sharing is about correct.
But at full load the motor with lower slip takes a higher share of the load than the motor with higher slip. The formula of the slip in the induction motor is given below. Slip Ns-NrNs100 In the above equation Ns is the synchronous speed in rpm whereas the Nr is the rotational speed in the rpm revolution for each second.
At no load the motor runs at say 1480 rpm. Slip at No load 133. At full load the speed of the motor is 1350 rpm.
Hence slip at full load 533. When the motor is so loaded that the rotor speed is reduced to 0 the value of Slip is 1. Hence value of Slip gradually increases from no-load to full load.
Electrical Induction Motors - Synchronous Speed. Example - Speed of Electric Motor. A motor with 4 poles runs with frequency 50 Hz.
The synchronous speed is 1500 rpm and the typical full load speed is 1450 rpm. The slip is the difference between synchronous and load speed - 50 rpm. Consider an example of 3 phase 4 pole induction motor rated for 1420 rpm.
At no load the motor runs at say 1480 rpm. Slip at No load 133. At full load the speed of the motor is 1350 rpm.
Hence slip at full load 533. When the motor is so loaded that the rotor speed is reduced to 0 the value of Slip is 1. When the motor reaches full speed the rotor poles are switched to short circuit.
During start-up the resistors reduce the field strength at the stator. As a result the inrush current is reduced. Another important advantage over squirrel-cage motors is higher starting torque.
The construction of slip ring induction motor is quite different compared to other induction motor. Slip rings Induction. Induction motor full load torque depend upon supply voltage slip and rotor resistance.
Starting torque can be increase by adding external resistance in. Tape should be avoided. The motor load can be estimated with slip measurements as shown in Equation 5 and the following example.
Load Output power as a of rated power Slip Synchronous speed - Measured speed in rpm S s Synchronous speed in rpm S r Nameplate full-load speed Load Slip S s S r x 100 Example. Phase-wound motors or wound motors or as slip-ring motors. Squirrel-cage Rotor Almost 90 per cent of induction motors are squirrel-cage type because this type of rotor has the simplest and most rugged construction imaginable and is almost indestructible.
The rotor consists of. The induction motor speed decreases by a few percent when the motor goes from no load to full-load operation. The full-load speed is a function of the motor design and power and is usually in the range of 9499 of the synchronous speed.
The difference is the slip. Since the short-circuited rotor windings have small resistance even a small slip induces a large current in the rotor and produces significant torque. At full rated load slip varies from more than 5 for small or special purpose motors to less than 1 for large motors.
2 The full-load slip of a 3-phase induction motor ranges from. 3 In a 3-phase induction motor the rotor speed is. 4 When the rotor of a 3-phase induction motor is blocked the slip is.
5 3-phase wound rotor motors are also calledmotors. An induction motor can be termed as a constant speed motor and the constant speed can only be achieved if the rotor speed is closed to the synchronous speed. Therefore a general-purpose induction motor is designed to operate in the low slip at full load in order to have good running performance.
Depending on the rating full load slip varies from 2 to 1. Such a motor has high starting current 5-8 times and low starting torque whereas for high HP motor the slip. Droops slightly as the load on the motor is increased.
The synchronous speed N s of the rotating magnetic field is calculated based on the number of poles P and the supply frequency f ie. Synchronous speed N s 120f rpm P Then slip S N s - N r x 100 Percent N s Normally the range of slip at full load is from 2 to 5 percent.