
Severe artifacts can result from improper preparation. SEM Sample Preparation.
For the examination of images of topography contrast from metal and ceramic specimens the only specimen preparation which is necessary is to ensure that the specimen is thoroughly degreased so as to avoid hydrocarbon contamination and in the case of.
Specimen preparation for sem. Published April 5 2017 Proper sample preparation plays an important role in obtaining the required information when using scanning electron microscopy SEM. You need to consider the samples size shape state and conductive properties prior to sample preparation. Ideally the smallest representative sample size is the one to use.
Mechanical preparation is the most common method for preparing these so-called materialographic or metallographic samples for microscopic examination. After embedding the samples are cut grinded and polished. Abrasive particles are used in successively finer steps to remove material from the surface until the required result is reached.
Standard SEM procedures for biological samples involve chemical fixation dryingdehydration mounting on a stub and coating with a metal eg. Chromium gold platinum etc for examination under a conventional SEM often referred as ambient temperature scanning electron microscopy ATSEM. Sample preparations are essential in scanning electron microscopy.
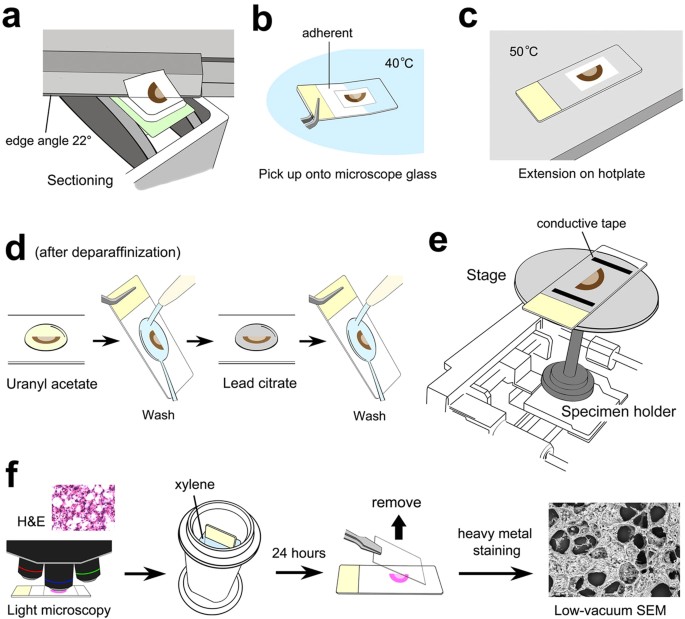
Flawed sample preparations can undermine the quality of results and lead to false conclusions. Thus the aim of this chapter is to equip researchers post graduate students and technicians with essential knowledge required to prepare samples for scanning electron microscopy SEM investigations in the life sciences. A new method freeze-cut-drying is introduced for preparing a soil specimen for microstructural analysis using scanning electron microscopy SEM.
With this method moisture in the specimen is removed by freeze-drying and an SEM observation surface is made by cutting the specimen at a temperature below freezing point. Specimen size depends very much on SEM model you use. High end microscopes can use in-lens observation for highest magnifications.
Specimen should be small a few mm in that case. The sample preparation point of view this is of major significance. For specimens that may change in vacuum biological tissues for instance this can be a major concern and newly developed accessories such as environ-mental cells 8 need to be added to the microscope.
For scanning electron microscopy of electrically insulating materials the. The first and perhaps most important step in the preparation process is fixation. In this step living tissue is chemically treated to stabilise it.
This kills the tissue sample at the same time. Its important to fix a sample as quickly as possible because as soon as tissue is removed from its natural environment it starts to change. Preparation often involves nothing more than mounting a small piece of the specimen in a suitable liquid on a glass slide and covering it with a glass coverslip.
The slide is then positioned on the specimen stage of the microscope and examined through the. Because of the microscopy requirements options for preparing specimens are limited to. Whole-mounts where an entire organism or structure is small enough or thin enough to be placed directly onto a microscope slide eg a small unicellular or multicellular organism or a membrane that can be stretched thinly on to a slide.
Following osmium fixation water is chemically extracted from the specimen using a graded series of ethanol. Typically the concentrations of ethanol used begin at 30 and proceed at 20 steps up. Preparation of Cement Paste Mortar and Concrete Sections Cement pastes mortars and concretes may be prepared in two ways.
A dry potting and B wet potting. Dry potting is used when the specimen has been dried before when drying shrinkage-related cracking is not of concern or when a rapid preparation is needed. Wet potting is used to.
Therefore bulk specimens can be examined in the SEM with a size limited only by considerations of accommodation in the specimen stage. For the examination of images of topography contrast from metal and ceramic specimens the only specimen preparation which is necessary is to ensure that the specimen is thoroughly degreased so as to avoid hydrocarbon contamination and in the case of. Before SEM characterization Clean and dry no outgassing.
Some particles have natural tendency to absorb moisture from regul environment. For biological samples critical drying to remove liquid without damaging the specimen. Always check recent published research papers to check on current techniques being used.
SEM Sample Preparation. Biological specimens must undergo a procedure known as critical drying in which moisture is removed from the sample without damaging or altering the features of the specimen. There is a chapter in your textbook dedicated to this topic.
Specimen preparation for SEM. The fully automatic drying of biological specimens such as pollen tissue plants insects for SEM analysis using the Leica EM CPD300 Critical Point Dryer. Proper preparation of flat-polished specimens for SEM is important.
Severe artifacts can result from improper preparation. The artifacts may appear as specific features in the backscattered electron mode eg cracks introduced in cutting or drying. They may cause loss of microstructural detail and prevent good resolution.