
The general linear model GLM Model. The p-values for the categorical IV and the interaction term are the same across models.
The SPSS GLM and multiple regression procedures give different p-values for the continuous IV.
Spss generalized linear model output interpretation. Notice the Sums of Squares column. The model is the overall total sums of squares 8550 in the numcorr variable that is explained by the two main effects and interaction considered together. The SS for Lecture room and Testing room are both 50 whereas the SS for the interaction is 8450.
We know the generalized linear models GLMs are a broad class of models. When fitting GLMs in R we need to specify which family function to use from a. The general linear model GLM is a flexible statistical model that incorporates normally distributed dependent variables and categorical or continuous independent variables.
The GLM procedure in SPSS allows you to specify general linear models through syntax or dialog boxes and presents the results in pivot tables so you can easily edit the output. In the SPSS output the Test of model effects table gives p-values of 0005 0343 0372 0035 and 0212 for variables ABCD and AC respectively. Complete the following steps to interpret a general linear model.
Key output includes the p-value the coefficients R 2 and the residual plots. The general linear model GLM Interaction. Interaction between a covariate and sex The e ect of the covariate depends on sex The di erence between men and women depends on the value of the covariate.
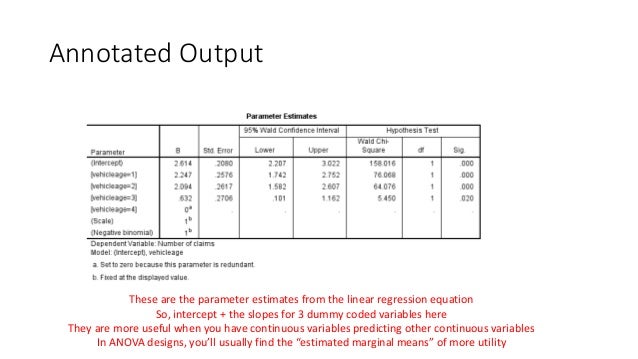
Karl B ChristensenhttppublicifsvsundkudkkachSPSS 6. The general linear model GLM Model. First for some reason instead of decimal places your output has commas not sure why that is happening but you can still interpret it.
All of the betas are part of a regression equation however because you are using binary data the program cannot solve it without a reference group. So SPSS chose 1 as your reference group for everything. This can be accomplished in a single run of generalized linear mixed models by building a model without a random effect and a series of 2-way interaction as fixed effects with Service type as one of the elements of each interaction.
Recall the Generalized Linear Mixed Models dialog and make sure the Random Effects settings are selected. The SPSS GLM and multiple regression procedures give different p-values for the continuous IV. The p-values for the categorical IV and the interaction term are the same across models.
This discrepancy only occurs when the interaction term is included in the models. Otherwise the output of the two procedures matches. We can ask SPSS to output the means but they are the marginal means.
Go to Analyze General Linear Model Univariate Options. Move the OVERALL yr_rnd2 and mealcat variables from the Factors and Factor Interactions field to the Display Means for field and click Continue. The syntax you obtain is as follows.
SPSS Regression Output II - Model Summary ANOVA. The figure below shows the model summary and the ANOVA tables in the regression output. R denotes the multiple correlation coefficient.
This is simply the Pearson correlation between the actual scores and those predicted by our regression model. R-square or R 2 is simply the squared multiple correlation. It is also the proportion of variance in the dependent variable accounted for by the entire regression model.
Generalized Linear Models Using SPSS. Generalized Linear Models can be fitted in SPSS using the Genlin procedure. This procedure allows you to fit models for binary outcomes ordinal outcomes and models for other distributions in the exponential family eg Poisson negative binomial gamma.
In this screencast Dawn Hawkins introduces the General Linear Model in SPSShttpoxfordly1oW4eUp. Model- This is the dialog box for defining the model both within-subjects and between-subjects. The default is a full factorial.
You can customize this to only include the interactions that you want. Sum of Squares is also set here. If there are no missing cells Type III is most commonly used.
SPSS Stepwise Regression - Model Summary SPSS built a model in 6 steps each of which adds a predictor to the equation. While more predictors are added adjusted r-square levels off. Adding a second predictor to the first raises it with 0087 but adding a sixth predictor to the previous 5 only results in a 0012 point increase.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. With a generalized linear model the situation is essentially the same but you may have to take into account the additional complexity of the link function a non-linear transformation depending on which scale you want to use to make your interpretation. Consider the case of logistic regression there are at least three scales available.
The betas exist on the logit log odds scale whereas pi the. The generalized linear model expands the general linear model so that the dependent variable is linearly related to the factors and covariates via a specified link function. Moreover the model allows for the dependent variable to have a non-normal distribution.
It covers widely used statistical models such as linear regression for normally.