
Pathological conditions associated with the male reproductive tract of the Sahel bucks. Testicular hypoplasia is relatively common in pets.
Histopathologic examination of the left testis revealed.
Testicular hypoplasia in humans. Congenital hypoplasia of testis 85437001. Congenital small testis 85437001. Congenital micro-orchidism 85437001 Recent clinical studies.
New insights into the expression of androgen and estrogen receptors of the appendix testis in congenital cryptorchidism. Sinopidis X Panagidis A. Pathological conditions associated with the male reproductive tract of the Sahel bucks.
Testicular hypoplasia in a bull persistently infected with bovine diarrhoea virus. Testicular hypoplasia in a hereford bull with 61 xxy karyotype. The bovine counterpart of human klinefelters syndrome.
Hypoplasia of the testes is a common condition and disorder of sexual development. The testis is smaller than normal for the age of the animal and it is often present in disorders such as cryptorchidism and other DSD. Hypoplasia of the testis and epididymis in an otherwise normal male is the focus here.
Possible causes include Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism Type 8. Check the full list of possible causes and conditions now. In humans testicular hypoplasia occurs in some syndromes Goeminne syndrome Klinefelter syndrome Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome or as a result of androgen deficiency.
Testicular hypoplasia is relatively common in pets. In infertile boars almost a quarter of the affected animals show testicular hypoplasia. In horses testicular atrophy is observed in up to 3 of stallions.
In young racehorses. In humans few testicular biopsies have been reported so far Semi-nara et al 1999. Brown et al 2003.
Ozisik et al 2003. Biopsy reported in an adult male was performed at the. Hypoplastic testes testes hypoplasia testicle hypoplasia testicular hypoplasia.
Underdevelopment or reduced size usually due to a reduced number of cells in the testicles. Testicular hypoplasia in a Hereford bull with 61XXY karyotype. The bovine counterpart of human Klinefelters syndrome.
Dunn HO Lein DH McEntee K. A Polled Hereford bull with good libido displayed gross testicular hypoplasia and azoospermia. His left testis weighed 236 g approximately 10 of the testis weight of normal Herefords.
Histopathologic examination of the left testis revealed. Testicular hypoplasia TH is a morphological and functional reproductive disorder that affects bulls around the world and consequently causes major economic losses due to reduced fertility rates. Despite the improvements in management practices to enhance performance of affected animals the use of hypoplastic animals for reproduction might contribute to expand the prevalence of.
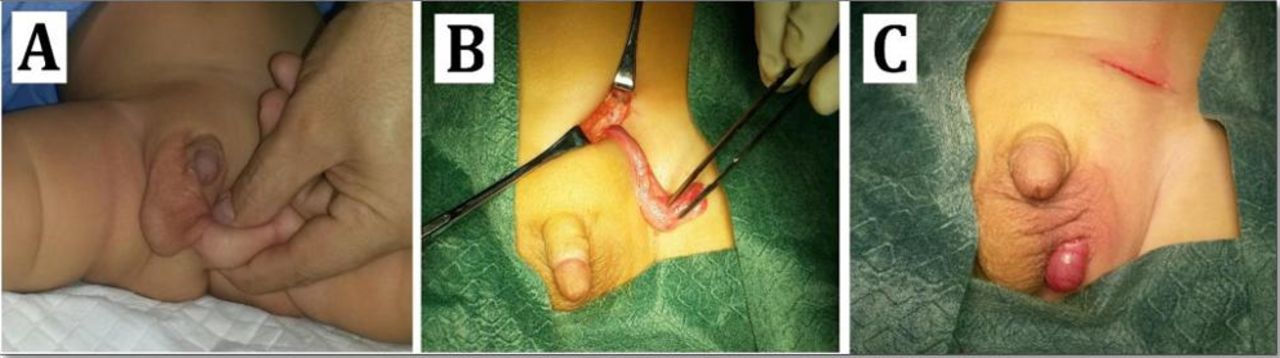
Testicular hypoplasia is a developmental disorder in which one or both testicles fail to reach normal size at sexual maturity. The small size and flabby consistency of these testicles is caused by poor development of sperm-producing tissue. Bilateral testicular hypoplasia was present and could be previously detected by the testicular volume and semen analysis being confirmed by histopathological evaluation of the testes and.
Further investigation of the 26 diethylstilbestrol-exposed men with testicular hypoplasia has revealed that 65 per cent had a history of cryptorchidism. Only 1 of the 6 placebo-exposed controls with testicular hypoplasia had a history of testicular maldescent. Although none of our Dieckmannâs lying-in study group has had carcinoma to date one must keep in mind the reported increased risk of.
Sequences of wild-type human LH receptor LHR and patient encoding amino acid residues 584-606 are presented. The altered sequence of 17 amino acids is not underlined. Insertion of a single.
The aim of this retrospective study was to assess the incidence and severity of tubular atrophyhypoplasia in the testes of 104 control Göttingen minipigs aged 45. Monochorionic diamniotic MCDA twins identified by ultrasound in early pregnancy are rarely dizygotic. Since Shouter et al.
First reported that MCDA twin pregnancies can occur in. Renal hypoplasia is a congenital reduction in the number of nephrons and oligomeganephronia a severe type of renal hypopla-sia in humans usually progresses to renal insufficiency with advanced age Drukker 2002. Oligonephropathy and other moder-ate reductions in.
The reduction in the testicular size may be attributed to non-genetic factors such as testicular degeneration or chronic orchitis 14 or genetic affections such as testicular hypoplasia 15. As reported in previous studies 141617 the bilateral marked reduction in both. The case described by Bogdanova et al.
2010 could be the first published case of possible freemartinism in human. Also the case of testicular hypoplasia Choi et al 2013 is comparable with.