
As the Polluter-Pays Principle is a fundamental principle of cost allocation its analysis covers a substantial part of the vast field of environmental resource allocation. The basis of this principle is that someone is financially responsible for the elimination of the pollution they cause.
Hayek discusses polluter pays principle PPP with students at Stanford in the 1970s in Inside the Hayek Equation.
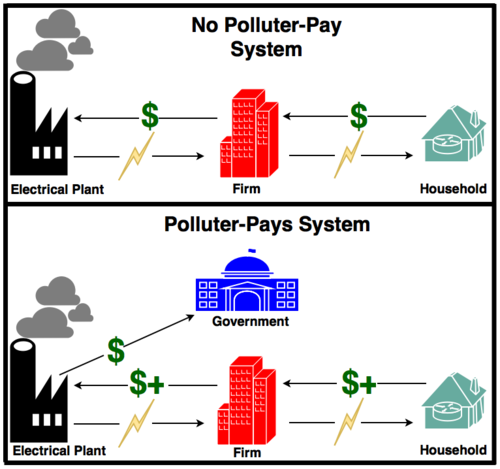
The polluter pays principle. The polluters pays principle is the commonly accepted practice that those who produce pollution should bear the costs of managing it to prevent damage to human health or the environment. The polluter pays principle is the commonly accepted practice that those who produce pollution should bear the costs of managing it to prevent damage to human health or the environment. For instance a factory that produces a potentially poisonous substance as a by-product of its activities is usually held responsible for its safe disposal.
Polluter-Pays Principle means that the polluter should be charged with the cost of whatever pollution prevention and control measures aredetermined by the public authoritieswhether preventive measures. The polluter pays principle PPP is a basic economic idea that firms or consumers should pay for the cost of the negative externality they create. The polluter pays principle usually refers to environmental costs but it could be extended to any external cost.
The costs of environmental problems are passed on to the community or to later generations unless the polluter pays principle is applied. The basis of this principle is that someone is financially responsible for the elimination of the pollution they cause. The Polluter Pays Principle.
A Proper Guide for Environmental Policy By Roy E. Cordato PhD The polluter pays principle states that whoever is responsible for damage to the environment should bear the costs associated with it1 Few people could disagree with what seems at first glance to be such a straightforward proposition. The polluter pays principle does not only apply if there is a real pollution in terms of harm or damage to private property andor the environment.
Most legal orders go beyond this interpretation. In the light of the precautionary principle environmental legislation. Title The polluter-pays principle in climate change law.
An economic appraisal abstract There is a lively debate among scholars and policymakers on whether either consumers or producers should be seen as responsible for pollution caused in the production and consumption of traded goods. Successive man-made disasters have seen the EU adopt rules to enforce the polluter pays principle on companies responsible for major environmental damage. The polluter pays principle definition.
The idea that the person or organization that causes pollution should pay to put right the. The polluter pays principle is based on the premise that whosoever causes damage to the environment must bear the costs associated with it. If a person contaminates the air or water bodies he should be made liable to pay the cost and take corrective measures such as purification of water bodies plantation of trees etc.
The polluter pays principle PPP or principle requires the polluter to bear the expense of preventing controlling and cleaning up pollution. Its main goals are cost allocation and cost internalization. In 1972 the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
As the Polluter-Pays Principle is a fundamental principle of cost allocation its analysis covers a substantial part of the vast field of environmental resource allocation. This report originally published in 1975 presents a selection of relevant theoretical and practical analyses now that the Polluter-Pays Principle must be regarded as a mainstay of Member countries environmental policies. Hayek discusses polluter pays principle PPP with students at Stanford in the 1970s in Inside the Hayek Equation.