
Anions could be transported across the membrane by cytochrome system. Diffusion A-level Biology OCR AQA Edexcel - YouTube.
Bioinformatics analysis has not determined any Ca 2-selective filters in plant ion channels but electrophysiological tests do reveal Ca 2 conductances in plant membranes.
Transport of ions across cell membrane in plants. Therefore it is an electro neutral pump. Electro genic pumps on the other hand transport ions involving net movement of charge across the membrane. For example H -ATPase found in plant and animal cells pumps out H with net movement of one positive charge.
The membrane itself contains polar groups and is therefore electrically charged. The transport of most ions occur more slowly than the non- electrolytes. But H OH penetrate all cell membranes easily.
The red cell is easily penetrated by Cl and HCO 3. Evidence for passive diffusional movements of ions across uninjured plasmalemmas of the cells of higher plants in a state of active absorption is neither extensive nor firm. This favors the view that active transport agents or carriers must mediate the movement of ions across these membranes.
Membrane vesicle traffic regulates ion transport by controlling the population and availability of transporters at the membrane and in some cases by direct binding with ion transporters. Transport of ions across cell membrane in plants biology discussion Get the answers you need now. Movement of virtually all molecules and ions across cellular membranes is mediated by selective membrane transport proteins embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
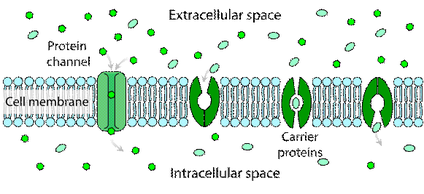
Because different cell types require different mixtures of low-molecular-weight compounds the plasma membrane of each cell type contains a specific set of transport proteins that allow only certain ions and molecules to cross. Transport across the membrane The chemical structure of the cell membrane makes it remarkably flexible the ideal boundary for rapidly growing and dividing cells. Yet the membrane is also a formidable barrier allowing some dissolved substances or solutes to pass while blocking others.
2Cytochrome Pump Salt Respiration or Electron Transport Theory. Anions could be transported across the membrane by cytochrome system. Energy is supplied by direct oxidation of respiratory intermediates.
This mechanism of ion transport is based on electrochemical gradient generated by electron transport. Secondary active transport The transport of substances against a concentration gradient involving energy to establish a gradient across the cell membrane utilizes the gradient to transport a molecule of interest up its concentration gradient. THE TRANSPORT MAY BE In the same direction SYMPORT In the opposite direction ANTIPORT.
Abstract and Figures The transport of solutes across cell mem- branes including organic nutrients such as sugar osmolytes ions or metabolic waste products is of extreme importance in all-. In addition there may be indirect interactions between ions as a result of their transport across the plasma membrane for example via effects on membrane potential through the movement of charge or via effects on the proton electrochemical gradient through the. Transport Across Cell Membranes.
Diffusion A-level Biology OCR AQA Edexcel - YouTube. Transport Across Cell Membranes. Diffusion A-level Biology OCR AQA Edexcel.
The physiological functions of Ca 2 are enabled by its orchestrated transport across cell membranes mediated by Ca 2-permeable ion channels Ca 2-ATPases and Ca 2 H exchangers. Bioinformatics analysis has not determined any Ca 2-selective filters in plant ion channels but electrophysiological tests do reveal Ca 2 conductances in plant membranes. There are a number of membrane-spanning proteins that are involved in the transport of different substances across membranes.
Channels have two states. They can be either open or closed and this change in shape is described as a conformational change. Movement across cell membranes Substances can move into and out of cells through the cell membrane.
The three main types of movement are diffusion osmosis and active transport. ATPases utilize the energy released upon hydrolysis of ATP to move ions across the plasma membrane against chemical and electrical gradients. In plant cells H -ATPases pump protons across the plasma membrane or tonoplast to acidify the extracellular matrix or the vacuole respectively Sze et al 1999.
Channel proteins facilitate the diffusion of water and ions down energetically favorable.