Relationship Between Risk V ulnerability. People vulnerable is complex and vulnerability can be both a risk factor for and an outcome of disasters.
Tangible and Intangible Vulnerability.
What is vulnerability and risk in disaster management. Vulnerability describes the characteristics and circumstances of a community system or asset that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard. There are many aspects of vulnerability arising from various physical social economic and environmental factors. Vulnerability and Risk in Disaster Management Published.
February 7 2016 Vulnerability is the extent to which a community structure services or geographic area is likely to be damaged or disrupted by the impact of particular hazard. Tangible and Intangible Vulnerability. People differ in their exposure to risk as a result of their social group gender ethnic or other identity age and other factors.
Vulnerability may also vary in its forms. Poverty for example may mean that housing is unable to withstand an earthquake or a hurricane or lack of preparedness may result in a slower response to a disaster leading to greater loss of life or prolonged suffering. Relationship Between Risk V ulnerability.
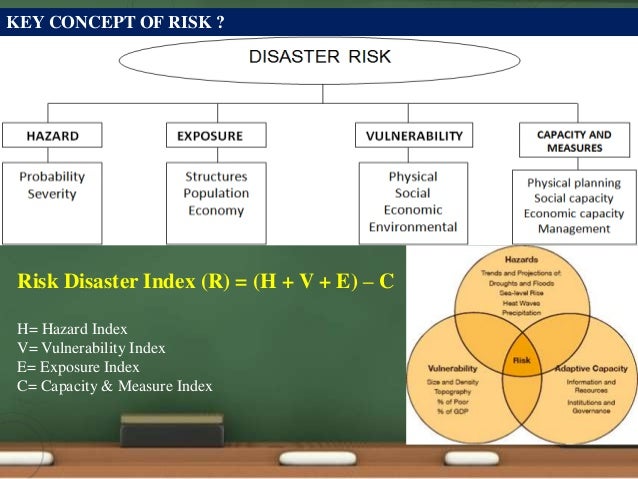
Risk is essentially the level of possibility that an action or act ivity will lead to le ad to a. Loss or to an undesired outcome when. Vulnerability and Risk What is Vulnerability Vulnerability describes the characteristics and circumstances of a community system or asset that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard.
There are many aspects of vulnerability arising from various physical social economic and environmental factors. Emphasis shifted to using vulnerability analysis as a tool in disaster management. In recent years a more comprehensive approach that of disaster risk management has emerged.
This approach has three distinct but interrelated components. Hazard assessment vulnerability analysis and. Assessing vulnerabilities and risks is a crucial task in any serious attempt to substantially reduce disaster losses.
Without an understanding of the relevant risks it is impossible to effectively prepare for or reduce them. This intensive course focuses on the entire vulnerability and risk assessment process from different methods for analysing risk to evaluating their results. Disaster Vulnerability and Resilience.
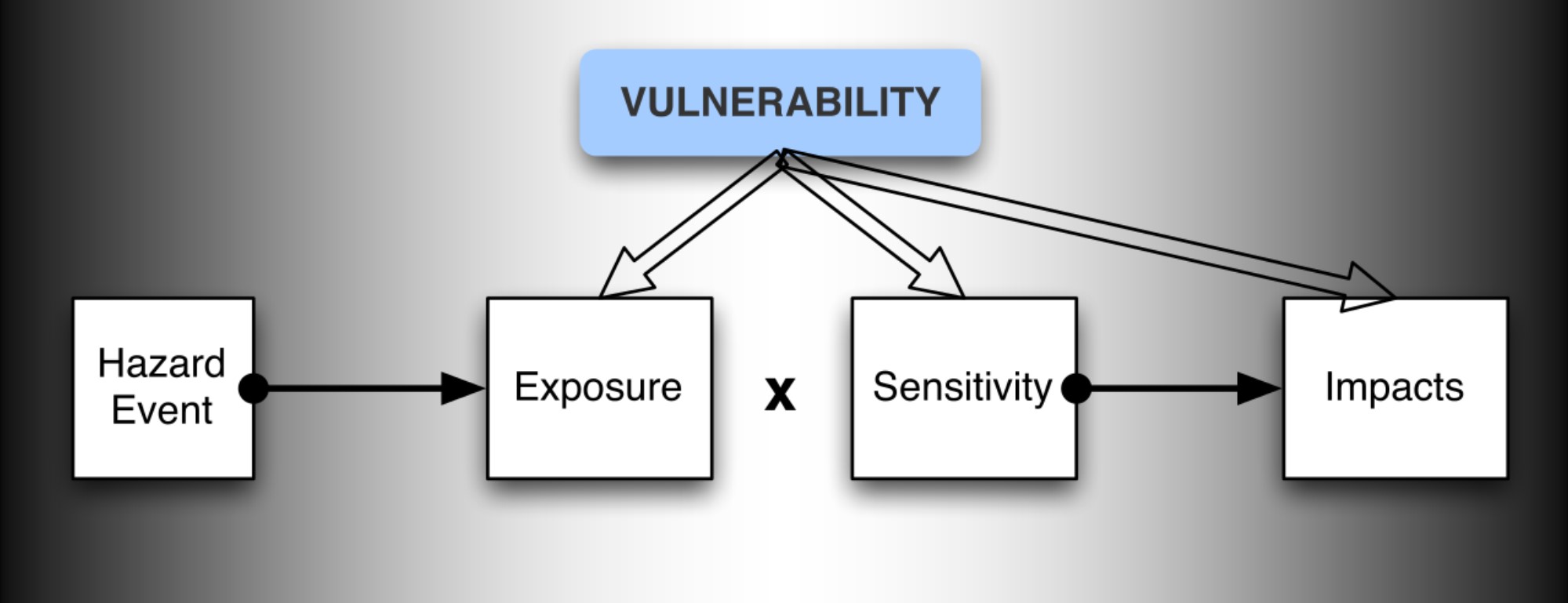
Theory Modelling and Prospective 8 risk to derive from the conjunction of vulnerability with hazard so that increases in either can worsen disaster risk and loss. The Pressure and Release Model The PAR model presents a progression of vulnerability consisting of root causes dynamic. For disaster risk management should be based on an understanding of disaster risk in all its dimensions of vulnerability capacity exposure of persons and assets hazard characteristics and the environment.
Such knowledge can be leveraged for the purpose of pre-disaster risk. Hazard exposure and vulnerability placed together will intersect and create what is known as potential loss or disaster risk he continued But we as citizens as well as the government and private sector can play a large role in reducing the impact of these three Hazard for instance can be decreased by early monitoring. A disaster is a result from the combination of hazard vulnerability and insufficient capacity or measures to reduce the potential chances of risk.
A disaster happens when a hazard impacts on the vulnerable population and causes damage casualties and disruption. 12 would give a better illustration of what a disaster is. People vulnerable is complex and vulnerability can be both a risk factor for and an outcome of disasters.
Vulnerability is discussed in Chapter 25 in relation to high-risk groups but for example poverty can put people at risk by forcing them to live in areas highly exposed to hazards and exposure to. Hazard risk and vulnerability HRV analyses form the basis of disaster management processes. Unfortunately to this point communities and regional districts have not.
Disaster vulnerability risk and capacity Vulnerability describes the characteristics and circumstances of a community system or asset that make it susceptible to the damaging effects of a hazard. There are many aspects of vulnerability arising from various physical social economic and environmental factors. The characteristics determined by physical social economic and environmental factors or processes which increase the susceptibility of an individual a community assets or systems to the impacts of hazards.
UNDRR Terminology 2017 Vulnerability is one of the defining components of disaster risk. From relief and response to vulnerability analysis to risk management has started influencing how disaster management programs are now being planned and financed. As it is becoming clear that the nature of peoples vulnerability is complex and varied linkages between poverty and vulnerability are being explored.
Disaster Risk assessment is a process to determine the nature and extent of such risk by analyzing hazards and evaluating existing conditions of vulnerability that together could potentially harm exposed people property services livelihoods and the environment on which they depend. Vulnerability Assessments and Risk Analyses allow for the identification of areas of critical concern and can help to guide mitigation efforts. There are many methodologies that exist today on how to conduct both risk and vulnerability assessments organizations such as the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration have even developed their own tools to aid this process.